The painful road to normalization - the FED will not rest until inflation is under control
In the second quarter of this year, the bond market will still be between the hammer and the hard place. While Federal Reserve it will pursue an aggressive monetary policy to curb inflation, the geopolitical situation will increase pressure on price increases and increase fears of a slowdown in economic growth. As a result, volatility will remain high, causing credit spreads to widen further.
The most important difference between the first and second quarter of 2022 is that, while at the beginning of the year bond yields increased due to expectations related to monetary policy, the markets now have to consider what actual actions will be taken by central banks. Political decisions will not be limited only to interest rate increases. They will also apply to other tools, such as balance sheet reduction, guidance on future interest rates or economic forecasts. If central banks fail market expectations, the risk of strengthening persistent inflation will increase; in turn, if central banks tighten the rate of the economy excessively, the risk of recession will increase.
About the Author
Althea Spinozzi, Marketing Manager, Saxo Bank. She joined the group Saxo Bank in 2017. Althea conducts research on fixed income instruments and works directly with clients to help them select and trade bonds. Due to his expertise in leveraged debt, he focuses particularly on high yield and corporate bonds with an attractive risk-to-return ratio.
Whether we are willing to admit it or not, we are entering a bear marketwhere profitability must increase significantly. In such an environment, traditionally safe investments such as US Treasury Bonds, will not protect investors seeking to diversify their portfolios. Duration (the so-called duration) will be even more toxic than ever as the starting point is historically low interest rates and there is no higher income to lean on. This is the result of many years of accommodative monetary policy which distorted the perception of risk and forced investors to take more risks due to both credit spread and bond duration.
Consequently, the potential for panic in the debt markets is increasing. The good news is that after this dark period of uncertainty and volatility, a new and better balance will be restored that will allow investors to rebuild their portfolios at much better market values.
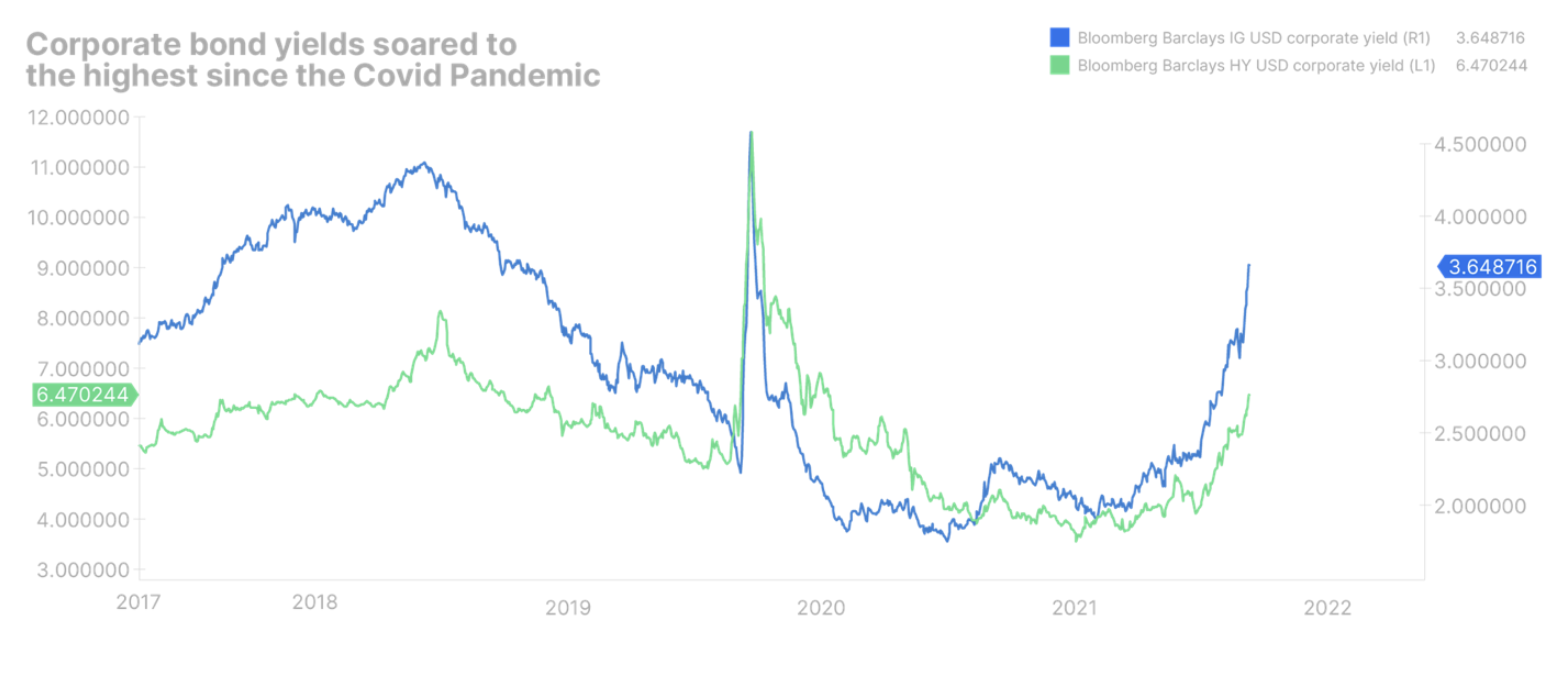
The Federal Reserve will not rest until inflation is brought under control
Since the beginning of this year US Treasury Bonds suffered the biggest losses compared to any year since 1974. Such poor results can be explained by expectations of interest rate increases in 2022. However, recently the situation has become more complex. Due to the increase in geopolitical tensions, investors faced the choice of high inflation or a slowdown in economic growth.
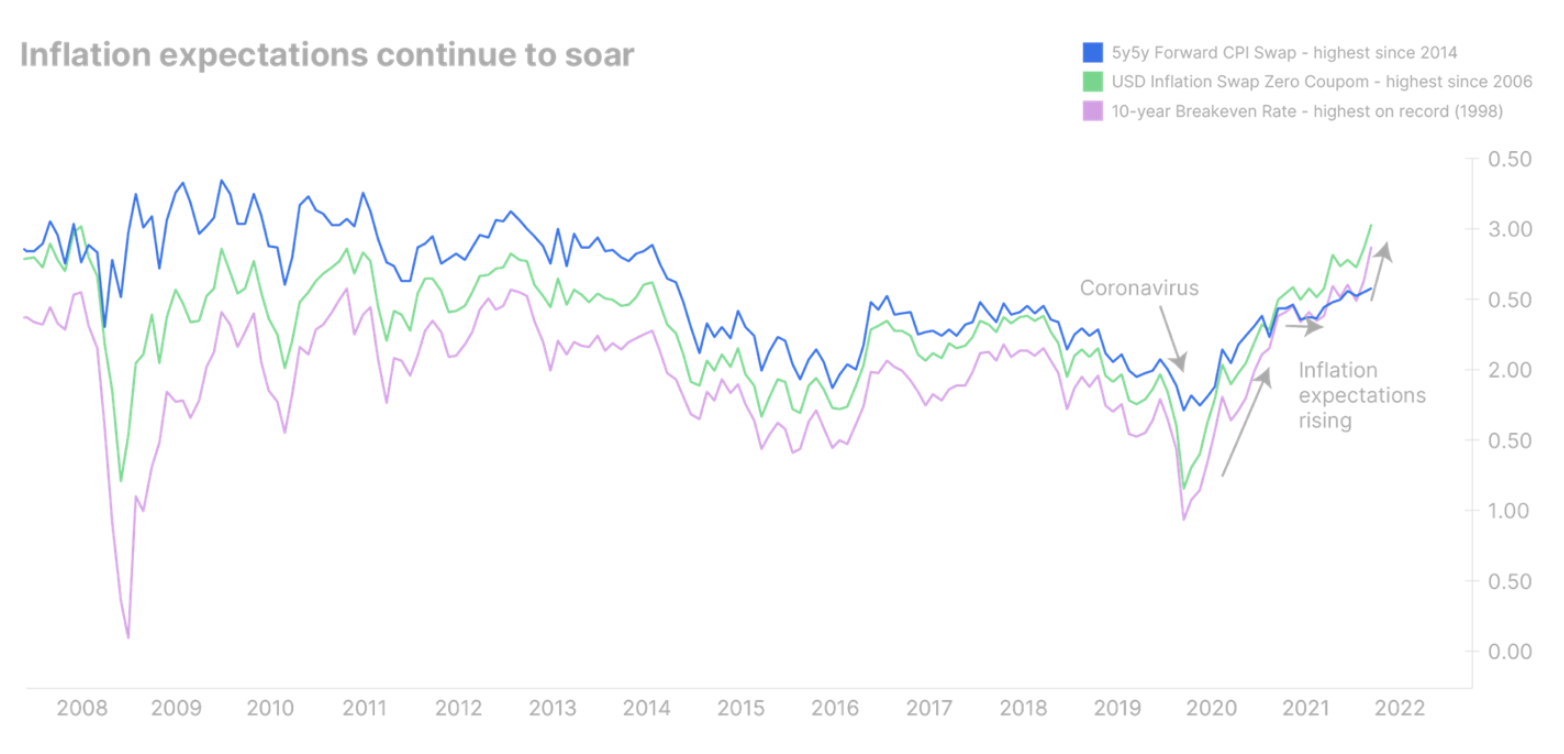
This is a huge problem for the Federal Reserve, which originally aimed to tighten the economy during an expansion period, when inflation was at its peak. At present, it is difficult to determine when this peak will take place, but an economic slowdown is inevitable. The Federal Reserve must redirect its efforts to address one of these two problems. In our opinion, this time the Fed will try to curb inflation at the expense of economic growth. In fact, US inflation expectations have recently hit record highs across the curve, indicating that high inflation is consolidating more than initially assumed.
However, fighting inflation is not as simple as it may seem. Although the current inflation has shocked the supply, the Federal Reserve is only able to contain demand. Even so, intervening in the form of higher interest rates to prevent inflation from rising further does make sense. However, higher rates require economic optimism, which is currently undermined due to the uncertainty surrounding the energy crisis. Therefore, the Fed's strategy of focusing on interest rate hikes could cause the yield curve to flatten further or even invert, which could spell a recession in the near future.
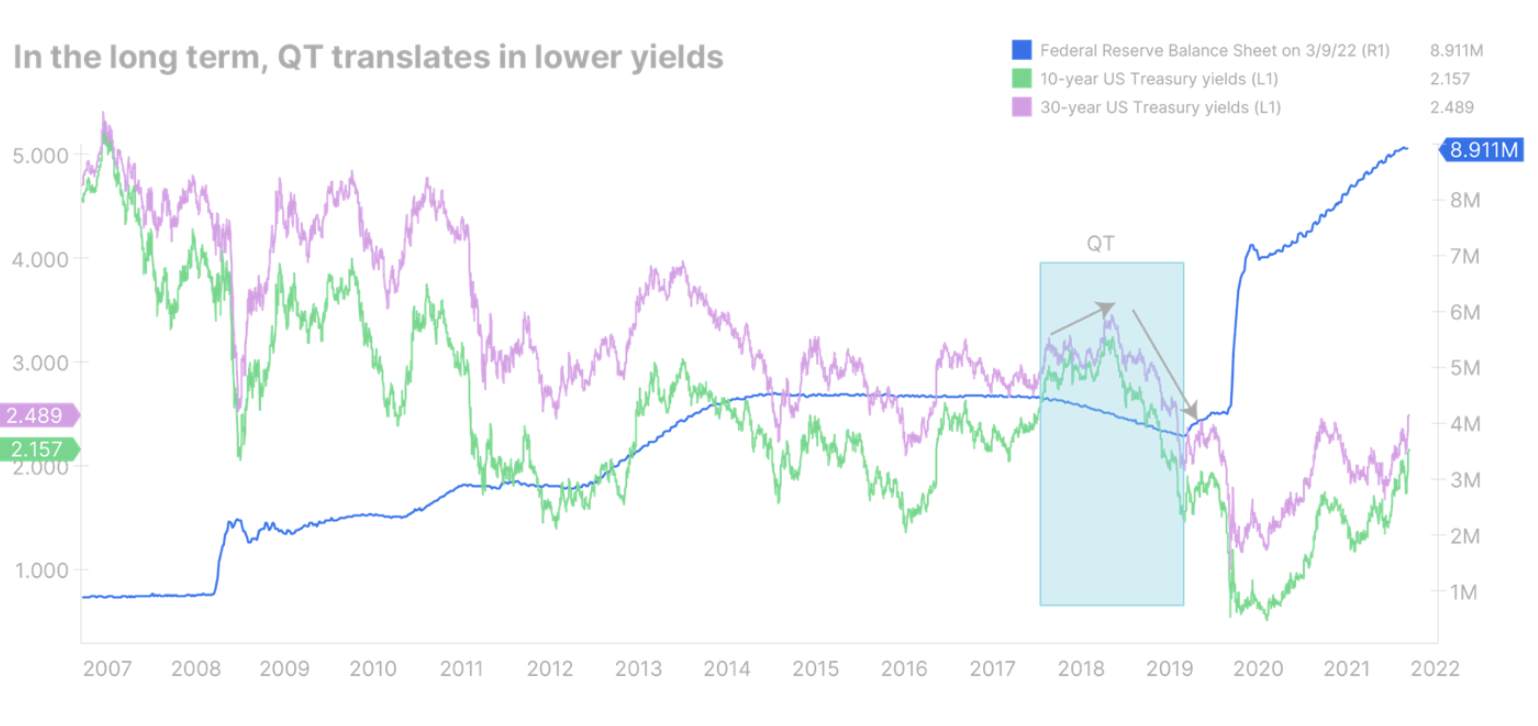
Therefore, we believe that sooner rather than later, the Fed will have to begin the process of reducing its balance sheet in order to raise long-term interest rates. It should be remembered, however, that in the past, a reduction in the balance sheet meant lowering interest rates in the long run. The best example is quantitative tightening. quantitative tightening, QT) in 2018-2019: although long-term rates initially increased, as market volatility increased, yields fell sharply.
History teaches us that central banks are better at controlling the short end of the yield curve than the long end because long-term rates are dependent on investors believing that the economy can withstand a Fed tightening path. It will be no different this time, and the Fed may have to recession to contain inflation.
Therefore, we expect US government bond yields to rise along the entire yield curve in the medium term, flattening it slightly. However, shortly after the start of a quantitative tightening, there may be a downward revision of long-term yields, causing a sudden flattening or even an inversion of the yield curve.
European bond yields will continue to rise and government bond yields will widen
In Europe, the situation will worsen before it gets better. The energy crisis is putting a lot of pressure on inflation. Therefore EBC it will not maintain its accommodative stance and will be forced to terminate fiscal stimulus earlier and start raising interest rates as early as September this year. The ECB risks that if it lags behind the Federal Reserve, the euro could devaluate further, leading to even higher inflation.
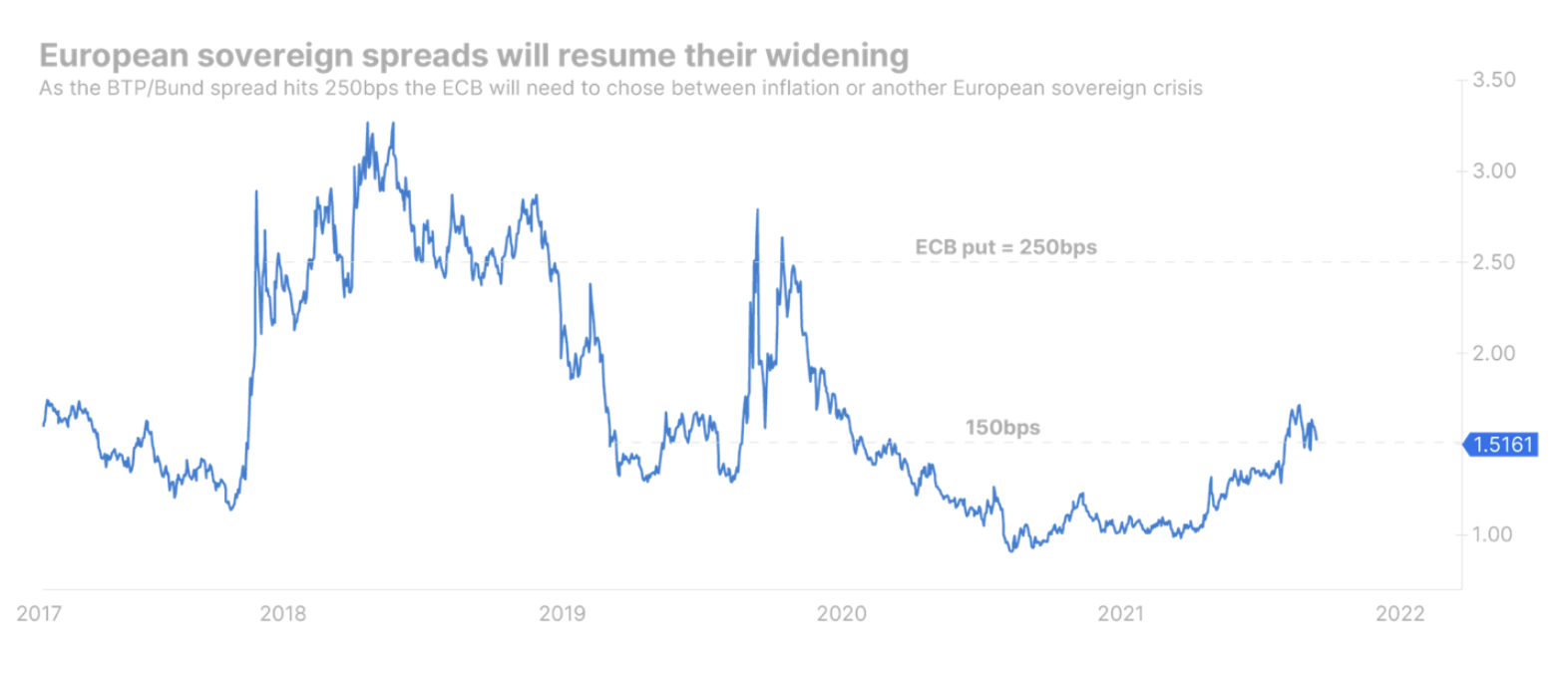
At the same time, European countries will try to finance their own defense spending and energy by increasing the issuance of treasury bonds, which will increase the pressure on the increase in profitability. The biggest problem is that this time around, the ECB will not be able to mitigate the effects of excessive indebtedness among Member States, as was the case with the Covid pandemic. Therefore, the volatility in the interest rate market will increase sharply. The scenario where 0,6-year German government bond yields increase to the XNUMX% target while European government bond spreads widen significantly is by no means unrealistic.
The much wider government bond spreads, apart from being politically problematic, are also a problem for the central bank's monetary tightening program as financial conditions will tighten at a faster pace in some countries than in others. We believe that the ECB will tolerate such a widening until the spread of Italian and German government bonds reaches 250 bp. At this point, the central bank may be forced to decide whether to prioritize inflation or economic growth.
Fiscal policy at EU level can prevent government bond spreads from widening rapidly. All Member States face the same problems with regard to energy and defense spending, so an EU defense and energy package, financed by issuing a common EU debt, would make sense; it would reduce volatility in the area of European government bonds, allowing the ECB to focus on inflation. However - as we have already seen on the occasion of the pandemic - reaching an agreement by EU Member States may prove to be a lengthy process, so it is unlikely that the peripheral countries will have access to such support already in QXNUMX.
Corporate bonds under more pressure
It is unlikely that the widening of corporate bond spreads would end. As central banks around the world increase interest rates, real yields will rise, which will tighten financial conditions even further. Even with real yields strongly negative, we are starting to see some alarm signals in the corporate bond area: widening spreads, volatile primary markets and a loss of investor risk appetite.
As volatility continues, weaker companies will find it increasingly difficult to access the primary bond market, which will increase the risk of refinancing and panic in the market.
All Saxo Bank's forecasts are available at this address.






















![Forex Club – Tax 9 – Settle tax on a foreign broker [Download the Application] Forex Club - Tax 9](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2024/02/Forex-Club-Podatek-9-184x120.jpg?v=1709046278)
![Trading View platform – solutions tailored to the needs of traders [Review] trading view review](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2024/03/trading-view-recenzja-184x120.jpg?v=1709558918)
![How to connect your FP Markets account to the Trading View platform [Guide] fp markets trading view](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2024/02/fp-markets-trading-view-184x120.jpg?v=1708677291)
![How to invest in ChatGPT and AI? Stocks and ETFs [Guide] how to invest in chatgpt and artificial intelligence](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2023/02/jak-inwestowac-w-chatgpt-i-sztuczna-inteligencje-184x120.jpg?v=1676364263)






![Izabela Górecka – “Success on the market depends not only on knowledge, but also on emotional stability” [Interview] Izabela Górecka - interview](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/Izabela-Gorecka-wywiad-184x120.jpg?v=1713870578)
![WeWork – the anatomy of the collapse of a company valued at $47 billion [WeWork, part II] wework bankruptcy story](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/wework-bankructwo-historia-184x120.jpg?v=1711729561)
![Adam Neumann – the man who screwed up Softbank [WeWork, part AND] adam neumann wework](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/adam-neumann-wework-184x120.jpg?v=1711728724)


![The most common mistakes of a beginner trader - Mr Yogi [VIDEO] Scalping - The most common mistakes of a beginner trader - VIDEO](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2024/03/Scalping-Najczestsze-bledy-poczatkujacego-tradera-VIDEO-184x120.jpg?v=1711601376)
![Learning patience: No position is also a position - Mr Yogi [VIDEO] Scalping - Learning patience - No position is also a position - VIDEO](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2024/03/Scalping-Nauka-cierpliwosci-Brak-pozycji-to-tez-pozycja-VIDEO-184x120.jpg?v=1710999249)
![When to exit a position and how to minimize losses - Mr Yogi [VIDEO] Scalping - When to exit a position and how to minimize losses - VIDEO](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2024/03/Scalping-Kiedy-wyjsc-z-pozycji-i-jak-minimalizowac-straty-VIDEO-184x120.jpg?v=1710336731)


















Leave a Response