Market correlations
Market correlations? What's this? Correlation from Latin means "interdependence", "mutual relationship" ...
So what are market correlations?
Translating this into the financial context, it means that financial markets are like connected dishes, where one segment of it is dependent on another and these mutual relationships are projected to some extent. The degree and direction of correlation is expressed by means of a correlation coefficient which oscillates in the range (-1; 1), where the values -1 and 1 indicate a strong, negative and positive relationship.
For example, a value of 1 means that one feature is completely dependent on the other and causes a change in the same direction (increase - increase), e.g. USD /JPY grow by 2%, quotations EUR /JPY they also grow at 2% at the same time.
The -1 value will mean the opposite situation, i.e. such a strong, negative correlation will occur when, for example, quoting EUR /USD will increase by 2%, and at the same time quotes USD/ CHF will drop by 2%.
READ NECESSARY: Filtering signals - how to choose the right opportunity to enter the position
A correlation ratio of 0 describes a situation where no relationship can be read, e.g. quotes EUR / GBP they increase by 2% and USD / PLN quotations have not changed.
Dependencies on the market
In financial markets, most financial instruments (and macroeconomic indicators) correlate to a greater or lesser extent. This can be summed up with the sentence - Everything can affect everything. However, let's not get crazy and pay attention to what is worth, i.e. the most important dependencies.
Currencies
On the Forex market, we trade currencies, where the value of one is always expressed relative to the other, with one currency being quoted in many other pairs. For example, a change in EUR / USD quotes affects both the value of the euro and the US dollar. This means that such a price fluctuation may to some extent trigger a change in quotations on both pairs, e.g. EUR/ JPY, like USD/ CHF. What will be the degree depends on the market trend itself, eg investors can sell mainly the dollar on a massive scale, which will cause a strong change to USD / CHF, and a small one to EUR / JPY.
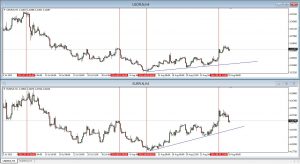
There are also more global dependencies, where a change in one market causes a change in another. It also happens that it only calls it in long time horizon or only under certain conditions.
Gold
It is widely accepted that the price of gold depends on the moods in global markets. If the situation is uncertain (crisis or threat of crisis), investors withdraw funds from riskier assets and invest them in the golden metal, which is perceived as a safe deposit for hard times (gold is a limited resource of a certain value). We are talking here about the negative correlation between gold and market sentiment.
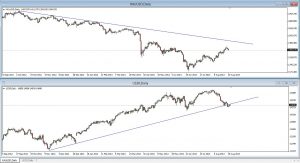
Other factors
Projects
You must always look at the stock market, like bonds, in a wider perspective. There is a long-term relationship with interest rates here. If the interest rates are regularly lowered, the chance for an increase in indices and share prices increases. This is due to the fact that a lower interest rate translates into less income from investments (and related instruments), while the cost of loan installments decreases. Therefore, investors are less and less profitable to hold funds in the bank and it is more and more profitable to take a loan. This may be aimed at increasing investors' engagement in the equity market in order to achieve satisfactory return rates. The increase in interest rates works in a similar way, which discourages the transfer of assets to this market.
treasuries
There is an inverse relationship between bond prices and interest rates. It's best to present it on an example. If we buy bonds with an interest rate of 4% and interest rates increase by 0,5%, the price of our bonds will fall due to the fact that new bonds will already earn interest by 4,5% (in theory). The reverse situation will occur when the interest rate drops.
Interest rates
True, hardly any broker gives the opportunity to play this instrument (although some offer futures on LIBOR and related) but there are a number of interesting correlations.
The change in inflation in the long term also affects the level of interest rates. If inflation starts to grow dynamically, one can expect that the central bank will start to raise interest rates in order to increase loan installments, which will reduce the scale of investment, which should translate into stabilizing prices.
READ ALSO: Do negative interest rates help economies?
A change in interest rates also causes a change in exchange rates (so it is also indirectly affected by inflation - look up). For example, increasing the interest rate in a given country increases the value of the national currency. This is due to the fact that with this change the interest rate on deposits in this currency increases. This encourages foreign investors to transfer assets to a given country (or even currency exchange).
Summation
The above points are only examples of occurring correlations. Market dependencies are much more and we strongly encourage you to research them yourself. Not everything works perfectly according to the theoretical scheme. Financial markets are a whole range of factors that are closely related to each other and changing one can affect the other, but changing the third can provoke the opposite effect.
Tools
The scale of correlation relations is constantly changing so it is worth monitoring these trends on a regular basis. The following tool can be used to test the correlation.
- CORRELATION indicator (available on ours forum) - thanks to it you can check the correlation relationships between any instruments on the MetaTrader platform.
- Built-in option for JForex platform, which allows you to superimpose several charts of different instruments on each other.
Literature
For more detailed information on market correlations and relationships, see John J. Murphy's book - "Inter-market technical analysis".






















![Forex Club – Tax 9 – Settle tax on a foreign broker [Download the Application] Forex Club - Tax 9](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2024/02/Forex-Club-Podatek-9-184x120.jpg?v=1709046278)
![Trading View platform – solutions tailored to the needs of traders [Review] trading view review](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2024/03/trading-view-recenzja-184x120.jpg?v=1709558918)
![How to connect your FP Markets account to the Trading View platform [Guide] fp markets trading view](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2024/02/fp-markets-trading-view-184x120.jpg?v=1708677291)
![How to invest in ChatGPT and AI? Stocks and ETFs [Guide] how to invest in chatgpt and artificial intelligence](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2023/02/jak-inwestowac-w-chatgpt-i-sztuczna-inteligencje-184x120.jpg?v=1676364263)



![Izabela Górecka – “Success on the market depends not only on knowledge, but also on emotional stability” [Interview] Izabela Górecka - interview](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/Izabela-Gorecka-wywiad-184x120.jpg?v=1713870578)
![WeWork – the anatomy of the collapse of a company valued at $47 billion [WeWork, part II] wework bankruptcy story](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/wework-bankructwo-historia-184x120.jpg?v=1711729561)
![Adam Neumann – the man who screwed up Softbank [WeWork, part AND] adam neumann wework](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/adam-neumann-wework-184x120.jpg?v=1711728724)





![The most common mistakes of a beginner trader - Mr Yogi [VIDEO] Scalping - The most common mistakes of a beginner trader - VIDEO](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2024/03/Scalping-Najczestsze-bledy-poczatkujacego-tradera-VIDEO-184x120.jpg?v=1711601376)
![Learning patience: No position is also a position - Mr Yogi [VIDEO] Scalping - Learning patience - No position is also a position - VIDEO](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2024/03/Scalping-Nauka-cierpliwosci-Brak-pozycji-to-tez-pozycja-VIDEO-184x120.jpg?v=1710999249)
![When to exit a position and how to minimize losses - Mr Yogi [VIDEO] Scalping - When to exit a position and how to minimize losses - VIDEO](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2024/03/Scalping-Kiedy-wyjsc-z-pozycji-i-jak-minimalizowac-straty-VIDEO-184x120.jpg?v=1710336731)




![Overlapping Charts [Indicator for MetaTrader 4] correlation overlapping mt4 charts](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2020/11/korelacja-nakladanie-wykresow-mt4-300x200.jpg?v=1604593531)











