Protective put – how to hedge against losses with options
The topic of today's article will be the option strategy - protective put. Most stock investors fear bear market periods. A bear market is a time when the supply side has an advantage over the market. As a result, there is a systematic decrease in the value of the stock portfolio, and the long-term investor has three options:
- Sell shares in the hope of buying them back later,
- Hold shares without worrying about the current valuation,
- Take advantage of hedging with derivatives.
Selling shares in the hope of repurchasing them later is a typical speculative strategy and is not advisable for the long-term investor. Speculation is always associated with taking on the risk of price changes. The long-term investor shouldn't sell stocks just because they "think" they might fall by a dozen or so percent over the next few months. There is a risk that such a deal will backfire on the investor who is left without a stock that has appreciated.
READ NECESSARY: What are options - an introduction
Holding stocks regardless of their current valuation seems to be the simplest strategy. It is only on paper. In fact, watching a stock portfolio lose a dozen or even several dozen percent due to a market downturn is very frustrating. This is especially painful for people who have invested most of their private wealth in the stock market. A long-term bear market can be very psychologically taxing for an investor holding his stock. Over time, the investor, exhausted by a shrinking portfolio, may sell at a low point, when the scale of pessimism is at its greatest.
An indirect method for the aforementioned two is the possibility of using derivatives hedging the portfolio. In this case, the investor holds the stocks he intends to hold long-term, and at the same time, he buys "insurance" in the event of a drop in the market price of the stock. The most commonly mentioned hedges are futures contracts or options on indices or specific stocks. One of the simplest strategies that allows you to hedge against declines and at the same time allow profits to grow is the protective put.
What is a protective put?
The protective put is one of the simplest options hedging strategies. It is based on the purchase of put options on shares that the investor wants to hedge. The assumption of the strategy is simple: the purchase of a put option is to minimize losses to an acceptable level. Of course, the cost of such an option depends on what such security should look like and under what conditions it is concluded.
In general, the protective put is a bullish strategy because the investor is still optimistic about the stock he owns, he just wants to limit the risk of a potential "paper" loss due to temporary market turmoil. Therefore, it is a combination of the optimism of a long-term investor with a "bearish" strategy, which is the purchase of a put option.
The investor using the protective put strategy may show a profit from the transaction in the event of a positive scenario. In the worst-case scenario, the loss is limited to the following level: option strike price – option premium paid.
By using this strategy, the investor knows in advance what is the maximum loss from the position. This allows for better portfolio risk management. If a profit is generated from the hedging transaction, the investor receives cash that can be used to remodel the portfolio.
In order to illustrate how the strategy works, it is worth using an example. An investor purchased 100 shares of XYZ company at the price of PLN 100. In order to protect himself against the decline, he purchased put options with an option premium of PLN 5 (per share). Below is a graph showing the results of the strategy.
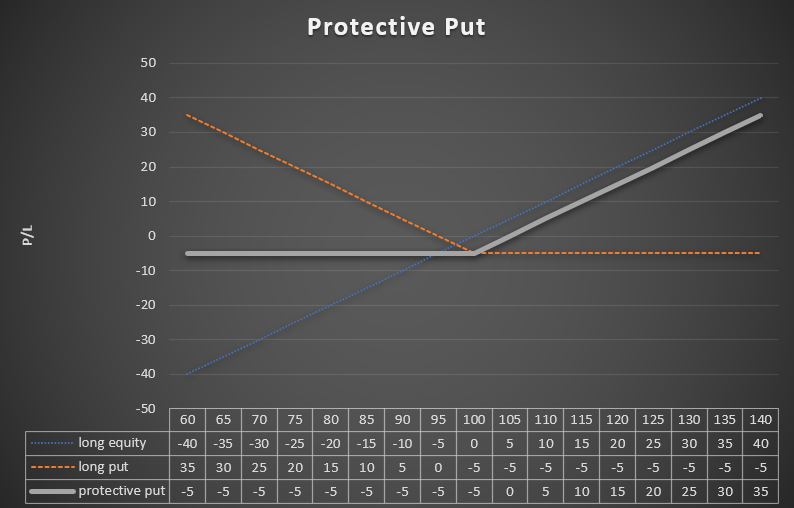
Source: own study
If the share price drops to PLN 60, the loss on the block of shares will amount to PLN 4000 (PLN 40 * 100 shares). The profit from the hedging transaction will amount to PLN 3500 (PLN 35 * 100 shares). Thus, the maximum portfolio loss in this example will be PLN 500 (PLN 5 * 100 shares). At the same time, the investor still has a chance to take a profit if the stock goes up. The investor will earn if the share price exceeds PLN 105 (share purchase price + option premium value).
How to use cash from a profitable hedging trade
If a put option transaction generates cash, then the investor must decide what to do with it. There are three main solutions that an investor can do with their cash:
- Acquire more discounted shares,
- Keep cash as an investment opportunity in other stocks,
- Cash withdrawal from the account.
Buying more discounted shares may be a good idea in a situation where the investor believes that the fall in the share price is due to external factors (market sentiment) rather than changing fundamentals. Thus, the decline in the share price left the investor still holding the same amount of shares in the company, but generated additional cash from the hedging transaction. He can therefore buy additional shares at a lower price. As a result, the average purchase price of shares decreases and the number of shares held by the investor increases, without the need to top up the account with an additional amount. The disadvantage of such a strategy is the increased exposure to a portfolio of stocks that are in a downtrend. It is possible that the investor mispriced the company and the drop in shares does not mean that they are currently valued at an attractive level.
Keeping cash for other investment opportunities is an interesting idea. Thanks to the strategy, the investor can buy shares of other companies that fell much more strongly and are now valued at more attractive levels. Second, having cash in your wallet is a good idea to amortize your portfolio value during a long-term bear market.
The third option is to withdraw cash from the account. This is an alternative to a dividend for retirees living only on their investment portfolio payouts (the 4% rule). For investors starting to build their net worth, a cash withdrawal is not the best solution.
Example transaction:
On June 30, 2022, an investor bought 300 Apple shares at an average price of $150. So the stock portfolio was worth $45. By August 000, 11, the company's share price increased to $2022. However, the investor began to fear that there was a high risk of a downward correction. He decided that he would try to secure the profits. For this reason, he decided to buy 3 put options with an exercise price of $170. The options expired on December 16, 2022. The option premium was $11,35. This meant that the trader had secured his position from $158,65. The investor could no longer lose on his stock portfolio.
Let's follow what happened in the following months. Until October 13 Apple shares dropped to $143. This meant a $7 loss per Apple share. At the same time, the price of the put option increased to $31,15. The profit from the hedging transaction was $19,8. So the total portfolio profit was $12,8. The investor decided to close the hedging position. As a result, $9 ($345 * 31,15) appeared in the account. The investor may choose to:
- Depositing cash on a brokerage account,
- Purchase of additional Apple shares.
Depositing cash on a brokerage account allows you to increase the liquidity of the portfolio and have funds to increase purchases in the event of a further decline in the share price. In the case of the growth scenario, the investor loses the opportunity for "cheap shopping".
If you choose to buy Apple shares, the investor will allocate $9 to buy 345 shares. Thanks to this decision, the stock portfolio increased to 65 shares. If, after additional purchases, Apple shares rise, the investor will increase the rate of return. Below is a table summarizing the different scenarios:
| Share price | 120$ | 140$ | 160$ | 180$ |
| 300 shares | $ 36 | $ 42 | $ 48 | $ 54 |
| 300 shares + cash | $ 45 | $ 51 | $ 57 | $ 63 |
| 365 shares | $ 43 | $ 51 | $ 58 | $ 65 |
Source: own study
Classic protection
This is the most common type of option hedging. It involves the purchase of a put option that gives exposure to the same number of shares as the investor has in the portfolio. Of course, the disadvantage of such a strategy is that if the investor owns an amount of shares that is not a multiple of 100, there will always be an inaccurate collateral match. For example, an investor owns 417 shares of Apple, the security with options can amount to either 4 options or 5 put options. Thus, the collateral will either be too small (400 share options) or too large (500 share options). Of course, the way out of this situation is to use delta hedging.
Delta protection
Secure your position with deltas is one of the possible methods of hedging a portfolio with options. The strategy is very simple, the idea is to make the change in the value of the option equal to the change in the value of the portfolio. This allows you to better protect your wallet, but at the cost of higher expenses. What does such a transaction look like on a simple example?
An investor owns 300 shares of Apple. This means that the delta of this position is 300 (1*300). Thus, a $1 increase in the price results in a $300 increase in the portfolio value. On the other hand, a fall in the price of Apple by $1 causes the value of the wallet to fall by $300. If the put delta is -0,5, then a $1 drop in Apple's price results in a put profit of $0,5.
For this reason, if an investor wants to hedge his position according to the principles of delta hedging, he needs to buy 6 put options with a delta of -0,5 each. Then a $1 drop in Apple's price results in a profit of $300 (0,5 * 600). Of course, such hedging is accurate only in the event of small price movements. As Apple's share price increases, the delta of the put option approaches zero, which means that the hedge will not cover future losses perfectly. On the other hand, if the share price decreases, the delta of the put option will start to increase towards the level of -1. This means that the investor's portfolio will grow during market declines.
In order to illustrate what exactly delta hedging is, we will use an example from the real market. The investor owns 500 Apple shares and on November 11, 2022 decided to hedge against the risk of a drop in the share price of the famous iPhone smartphone manufacturer. To do this, he bought put options expiring on December 16 with an exercise price of $150. The delta of this option on November 11 was equal to -0,478. This meant that buying 10 put options (exposure to 1000 Apple shares) gives a delta of -478 (1000*-0,478). This means that the delta of the entire position is now 22. A $1 drop in Apple's price results in a loss of $22 (instead of $500 before hedging. The hedging trade alone cost $5900 ($5,90 * 1000 shares). It is worth mentioning that the value of the portfolio is approximately $75, so the cost of hedging was 000% of the portfolio value.
An important factor that allows you to study the impact of price changes on the size of the option is greek gamma. Therefore, the solution may be the use of delta-gamma hedging, which neutralizes the impact of price changes on the delta level.
Of course, in addition to the delta and gamma effects, it is worth considering that the option price is also affected by theta (the effect of time on the option price) and vega (the effect of implied volatility on the option price).
Protective put vs married put
Both strategies use buying put options to hedge their market exposure. The only difference between a protective put and a married put is the time at which the investor purchases the put option. In the case of a protective put, the investor acquires the option after having previously acquired a stock portfolio. Thus, it is a situation in which a put option is purchased in order to protect the portfolio against potential risk (e.g. presidential elections, financial results). Often, a protective put strategy is used to hedge most of the profits already made from the strategy. A married put, on the other hand, is a situation in which an investor buys shares and put options at the same time. Therefore, he hedges himself at the start, trying to minimize potential losses.
Protective put vs long call
Another option is to buy a call instead of holding a basket of stocks secured by a put option. Buying a call option instead of a protective put strategy is an interesting idea for long-term investors. Then you can buy a deep ITM option with a long expiration period (so-called LEAPS). This solution allows you to reduce the initial investment, because even a deep ITM option (i.e. in money) usually has an option premium of 30% to 50% of the nominal value of the contract. At the same time, the delta itself would be above 0,9.
An example is the purchase of an Apple stock option with an exercise price of $80 and an option premium of $81. The delta of this option was 11 on November 2022, 0,931. The BEP level is $161, which is 7,73% more than the current share price. The option expires on January 17, 2025. The maximum portfolio loss is $81. When investing in stocks, the investor risks $149,44 (market price). The advantage of the long call LEAPS strategy is that there is no need to conclude two transactions and the investor has a lot of time until the option expires for the growth scenario to materialize. The disadvantage of the trade is that the maximum loss is much lower than with a protective put. On the other hand, it is concluded for a much shorter period.
Protective put vs covered call
Another type of hedging strategy is to use a strategy called covered call. It consists in issuing call options on shares that the investor already owns. Earnings for the investor appear when the share price drops slightly or does not increase. Then the call option expires worthless, which is pure profit for the investor. Covered call can therefore be a strategy that protects the investor's portfolio (up to a certain point). If an investor wants to hedge against the risk of a larger drop, they simply start writing call options, which are ITMs. They therefore have a time bonus and intrinsic value.
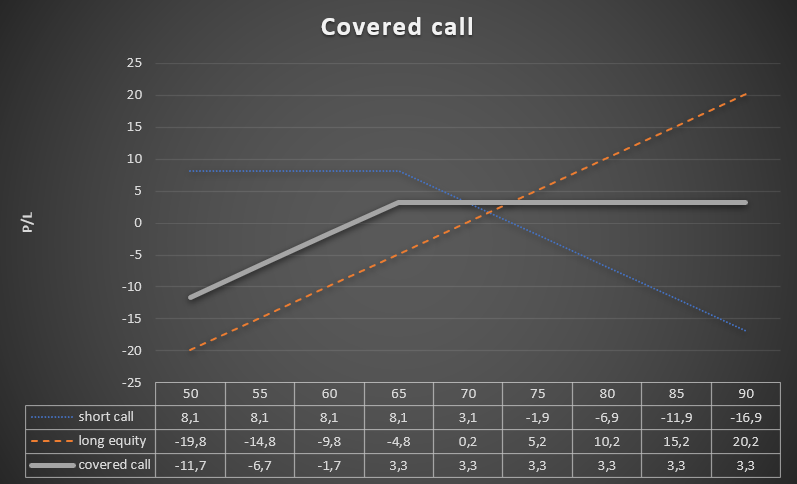
The investor owns 300 Euronext NV shares, which were traded at €14 on November 69,8. The investor expects a downward correction in the next few months. He decided that before the risk of a drop in the price he would use a call option issued on his portfolio of Euronext shares. The investor expects a decrease of the maximum by a dozen or so percent. For this reason, he issues 3 call options expiring on June 16, 2022 with an exercise price of €65. The bonus received was €8,10. This means that the investor is protected against a decline in the share price to €61,7. Thus, the investor is protected until the share price drops by approximately 11,6%. At the same time, the maximum profit per trade will be 4,72% (i.e. €73,1/€69,8). The advantage of using the covered call strategy is that the investor does not have to incur additional costs. On the other hand, the disadvantage is that the collateral is not full (in this case only up to 11,6%), and the future potential for generating profits is significantly limited.
Source: own study
In comparison, if a trader wanted to hedge his position with a put option, he could buy the June put options with a strike price of €70 and pay €6 for it. This means that the investor can suffer a maximum loss of 8,31%, and will start to generate profit only when the price exceeds €75,8 (the rate must increase by 8,60%). As you can see, hedging with put options is not perfect.
Protective put vs collar
Necklace is a strategy that "combines" protective put and covered call. The strategy is to buy put options on stocks you own while putting call options on the same stocks. This strategy allows you to reduce the cost of hedging, which is the purchase of put options. The disadvantage of this strategy is the "cutting off" of the profit potential due to issuing the call option. A collar strategy can be a good idea to protect your trading profits.
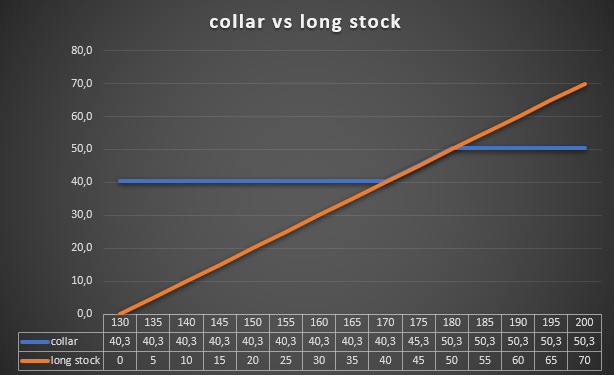
An example is an investment in Apple shares. In June 2022, an investor purchased 300 shares of this company at an average price of $130. In mid-August 18, the company's share price rose to $174,5. The investor still wants to be an Apple shareholder, but fears a correction. In order to hedge his position, he bought 3 put options with an exercise price of $170 and expiring on December 16, 2022. The cost of one option was $9,25 (per share), so the total cost of hedging was $2775. This means that the investor was protecting his portfolio from falling below $160,75. The buyer of the put option decided to reduce his hedging strategy cost. For this purpose, on the same day, he issued 3 call options with an exercise price of $180. He received $9,56 per share for it. This meant that the strategy was at no monetary cost. The investor received even $93 [i.e. ($9,56-$9,25)*300].
Source: own study
Summation
Key conclusions from the strategy:
- Protective put is a portfolio risk management strategy that uses options to protect against potential declines in value, stocks, indices, commodity prices or currencies.
- The cost of the defensive strategy depends on the duration of the option and its strike price.
- The protective put allows theoretically unlimited profits, because the strategy, unlike the collar, does not limit the maximum level of profit.
- A strategy similar to the protective put is the married put. Both strategies are used to protect against the decline of a long position in put options.
- The cash generated from the hedging transaction can be used to: purchase more shares, put cash on the account, withdraw funds.
Do you know that…?
Saxo Bank is one of the few brokers Forex , offering vanilla options. The investor has a total of over 1200 options (currencies, stocks, indices, interest rates, raw materials) at his disposal. CHECK






















![Forex Club – Tax 9 – Settle tax on a foreign broker [Download the Application] Forex Club - Tax 9](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2024/02/Forex-Club-Podatek-9-184x120.jpg?v=1709046278)
![Trading View platform – solutions tailored to the needs of traders [Review] trading view review](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2024/03/trading-view-recenzja-184x120.jpg?v=1709558918)
![How to connect your FP Markets account to the Trading View platform [Guide] fp markets trading view](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2024/02/fp-markets-trading-view-184x120.jpg?v=1708677291)
![How to invest in ChatGPT and AI? Stocks and ETFs [Guide] how to invest in chatgpt and artificial intelligence](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2023/02/jak-inwestowac-w-chatgpt-i-sztuczna-inteligencje-184x120.jpg?v=1676364263)


![WeWork – the anatomy of the collapse of a company valued at $47 billion [WeWork, part II] wework bankruptcy story](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/wework-bankructwo-historia-184x120.jpg?v=1711729561)
![Adam Neumann – the man who screwed up Softbank [WeWork, part AND] adam neumann wework](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/adam-neumann-wework-184x120.jpg?v=1711728724)





![How to transfer shares to another brokerage office [Procedure description] how to transfer shares to another brokerage house](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2024/03/jak-przeniesc-akcje-do-innego-biura-maklerskiego-184x120.jpg?v=1709556924)

![The most common mistakes of a beginner trader - Mr Yogi [VIDEO] Scalping - The most common mistakes of a beginner trader - VIDEO](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2024/03/Scalping-Najczestsze-bledy-poczatkujacego-tradera-VIDEO-184x120.jpg?v=1711601376)
![Learning patience: No position is also a position - Mr Yogi [VIDEO] Scalping - Learning patience - No position is also a position - VIDEO](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2024/03/Scalping-Nauka-cierpliwosci-Brak-pozycji-to-tez-pozycja-VIDEO-184x120.jpg?v=1710999249)
![When to exit a position and how to minimize losses - Mr Yogi [VIDEO] Scalping - When to exit a position and how to minimize losses - VIDEO](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2024/03/Scalping-Kiedy-wyjsc-z-pozycji-i-jak-minimalizowac-straty-VIDEO-184x120.jpg?v=1710336731)




![How to invest in ChatGPT and AI? Stocks and ETFs [Guide] how to invest in chatgpt and artificial intelligence](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2023/02/jak-inwestowac-w-chatgpt-i-sztuczna-inteligencje-300x200.jpg?v=1676364263)



