Mexico - one of the largest economies of Latin America [part AND]
For many European people, Mexico is a country that is associated with tortillas, tequila and drug cartels. History lovers will also mention pre-Columbian civilizations such as the Olmecs, Aztecs and Mayans.
However, Mexico is the second largest market in Latin America and the Caribbean (Brazil is the leader). It is also one of the largest economies in the world. Mexico is also one of the most developed economies in Latin America (in terms of GDP per capita after purchasing power). From 1994 to 2020, Mexico was together with the United States and Canada in NAFTA (North American Free Trade Agreement). From mid-2020, the treaty was renegotiated. As a result, a new CUSMA (Canada - United States - Mexico Agreement) was created.
Check it out: Australian companies - an interesting idea for portfolio diversification
Country development indicators
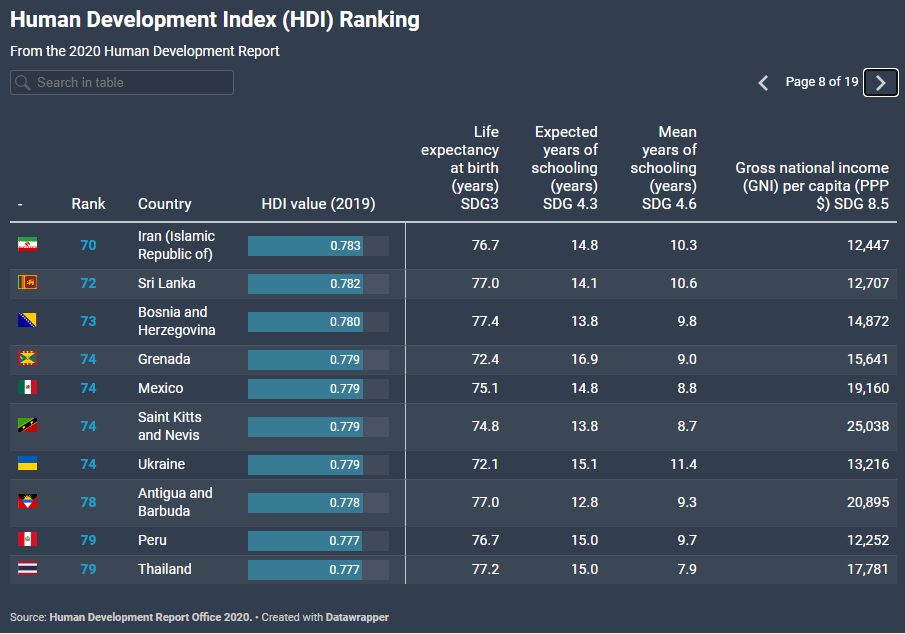
Mexico, despite its proximity to the American economy, is still ranked it is for developing countries. It is also visible in the HDI (Human Developmet Index). The index assesses countries in terms of: expected quality of life, quality of education, and national income per person. In 2019, Mexico was ranked 74th (on par with Ukraine). As a result, Mexico is located lower, among others from Romania (49), Russia (52), Uruguay (55) and Polish (35).
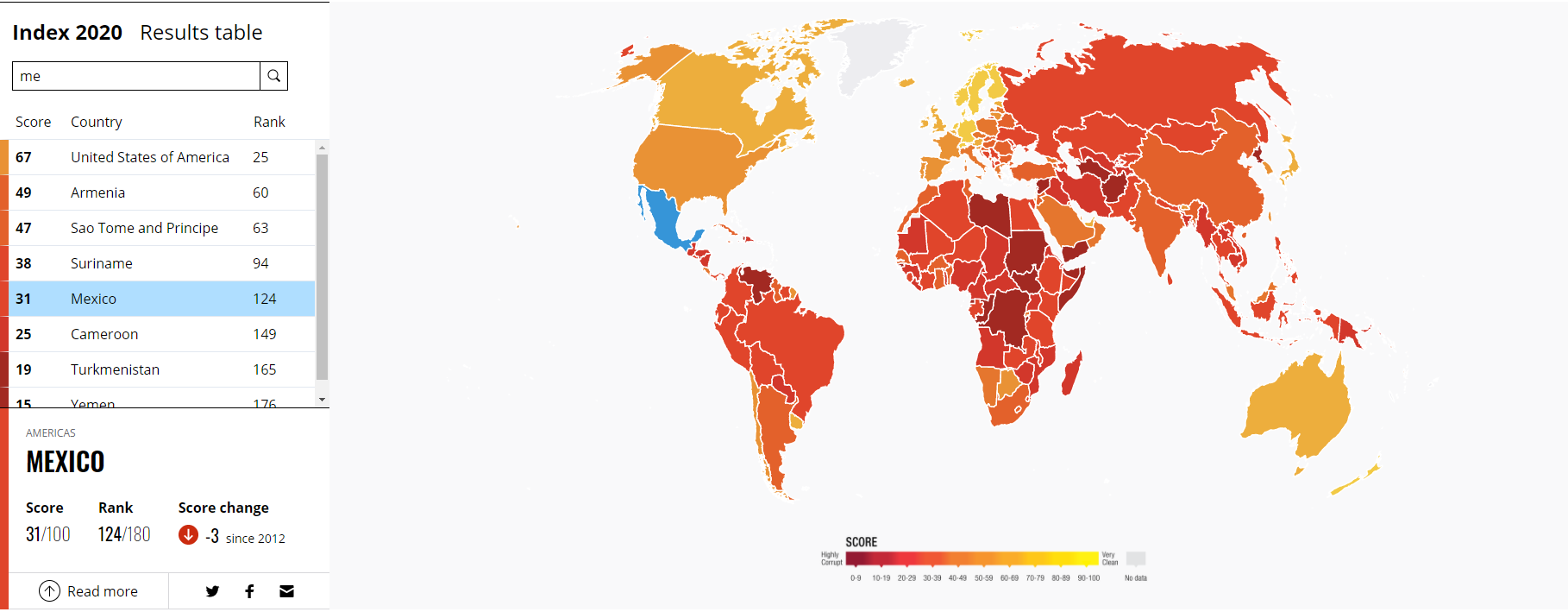
Mexico is not the best in the ranking Corruption Perceptions Index (Corruption Perception Index) by Transparency International. Mexico's economy in 2020 scored 31 points, which put the country in 124th place, on a par with Kyrgyzstan, Pakistan and Bolivia. Mexico was behind Brazil (94th place), Chile (25th) and Argentina (78th).
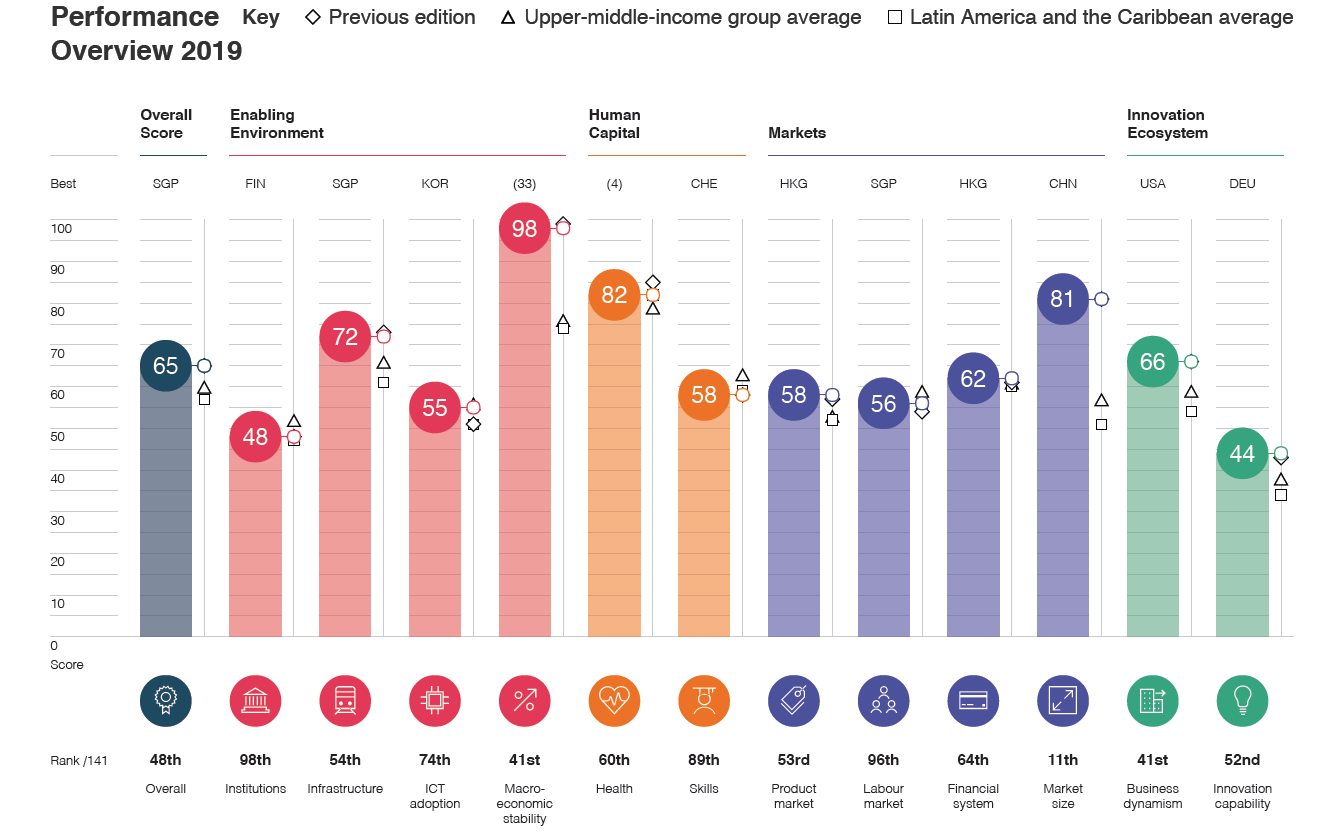
In the case of the competitiveness index Global Competitiveness Index Mexico is already doing better than the CPI. At the end of 2019, the country was ranked 48th. The weaknesses are institutions (position 98) and the labor market (position 96). Mexico is doing quite well in terms of market size (11th place), which is due to huge population.
The overall competitiveness index ranks Mexico behind Chile (33) but ahead of Uruguay (54), Colombia (57) and Brazil (71).
It is also worth remembering that Mexico is a country of high inequality. This is clearly seen in the Gini index, which determines income inequality. It takes values from 0 to 1. The higher the index, the greater the stratification in the society. In the case of Mexico, the Gini coefficient was 0,454 in 2018 according to the World Bank. Much more than in Poland (0,297), but less than in Brazil (0,539). The richest Mexican is Carlos Slim, whose net worth in October 2020 was estimated at $ 53,7 billion
Mexican Peso (MXN)
The Mexican Peso is a major emerging currency. The current peso was introduced in 1993 as the "new peso" at a ratio of 1: 1000 old pesos. Before the currency reform, the Mexican peso had the abbreviation MXP. Monetary policy is conducted by the Bank de Mexico.
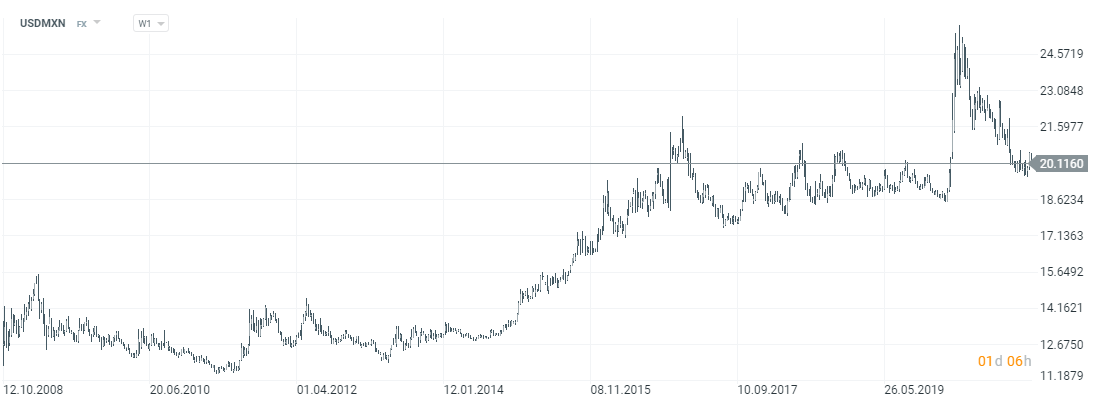
Chart of the USD / MXN currency pair, interval W1. Source: xNUMX XTB.
Interest rates - monetary policy
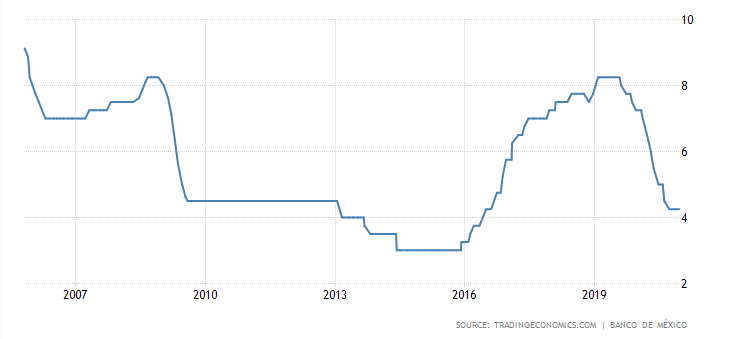
From 2016 to 2019, the central bank raised interest rates to control inflation. At the beginning of 2019, the rate was over 8%. The economic downturn forced the Bank de Mexico to cut interest rates. Currently, it is 4,25%.
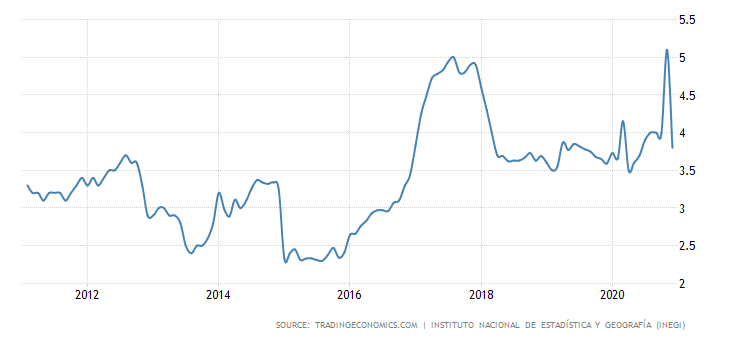
Mexico, compared to many Latin American countries, has no problems with keeping inflation in check. Over the last 10 years, inflation has generally fluctuated between 2,5% and 4%, with some spikes around 5%.
Economic development over the years
Mexico has one of the largest economies in the world. According to data World Bank in 2019, the Mexican economy was the 1th largest in the world in terms of GDP ($ 258 billion). It meant less than 1,43% share in the global GDP. Taking into account the purchasing power parity, Mexico was 12th in the world, between Italy (11th) and Turkey (13).
Be sure to read: Macroeconomic indicators: GDP, CPI inflation
Australia's economic growth has been very strong over the past 28 years. Between 1991 and 2019, GDP growth in purchasing power parity increased by 4,66% annually. The world grew at a slightly faster pace. This resulted in a slight decrease in the share of the Mexican economy in world GDP.
The mid 90's was very hard on the Mexican economy. The tequila crisis hit the country's economy hard. In 1995, GDP fell by 7%, while real wages fell by more than 13,5%. At the same time, unemployment increased from 4% to 3,7%. After Mexico's problems, the so-called The Tequila effect, which led to lower investor confidence in many Latin American countries (eg Argentina).
Below is a compilation of the World Bank.
|
GDP (PPP) |
1991 |
2005 |
2010 |
2019 |
|
Meksyk |
$ 732 billion |
$ 1 billion |
$ 1 billion |
$ 2 billion |
|
World |
$ 30 billion |
$ 66 billion |
$ 89 billion |
$ 135 billion |
|
% share of world GDP |
2,37% |
2,02% |
1,95% |
1,93% |
The table below shows that the years 1991-2019 were not part of the "golden age". Mexico did not manage to catch up with the United States. The fact that you can "run faster" is demonstrated by the example of Poland, which caught up with Mexico in terms of GDP (PPP) per capita and then overtook Mexico. Below is a compilation of the World Bank:
|
GDP (PPP) per person |
1991 |
2005 |
2010 |
2019 |
|
Meksyk |
8 560 $ |
12 658 $ |
15 261 $ |
$ 20 |
|
USA |
$ 24 |
$ 44 |
$ 48 |
$ 65 |
|
Poland |
$ 5 |
13 897 $ |
$ 21 |
$ 34 |
|
Brazylia |
$ 6 |
$ 10 |
$ 14 |
$ 15 |
|
World |
$ 5 |
$ 10 |
$ 12 |
$ 17 |
|
% US |
35,17% |
28,69% |
31,49% |
31,61% |
|
% Of Brazil |
123,88% |
115,19% |
106,72% |
134,52% |
|
% Poland |
144,74% |
91,08% |
72,37% |
59,78% |
In the case of Mexico, most of the economy is based on services, where more than 64% of GDP is produced. Industry accounts for approximately 32% of the Gross Domestic Product. In Mexico, sectors such as automotive, household appliances, food, tobacco, petrochemical, textile and steel are developed.
Unemployment rate
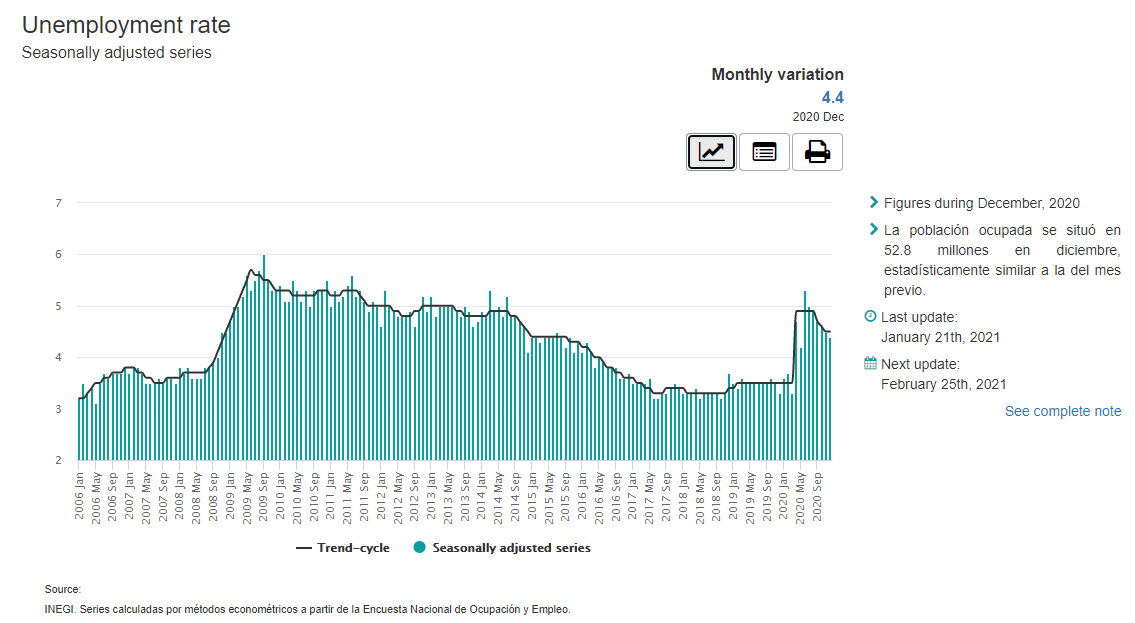
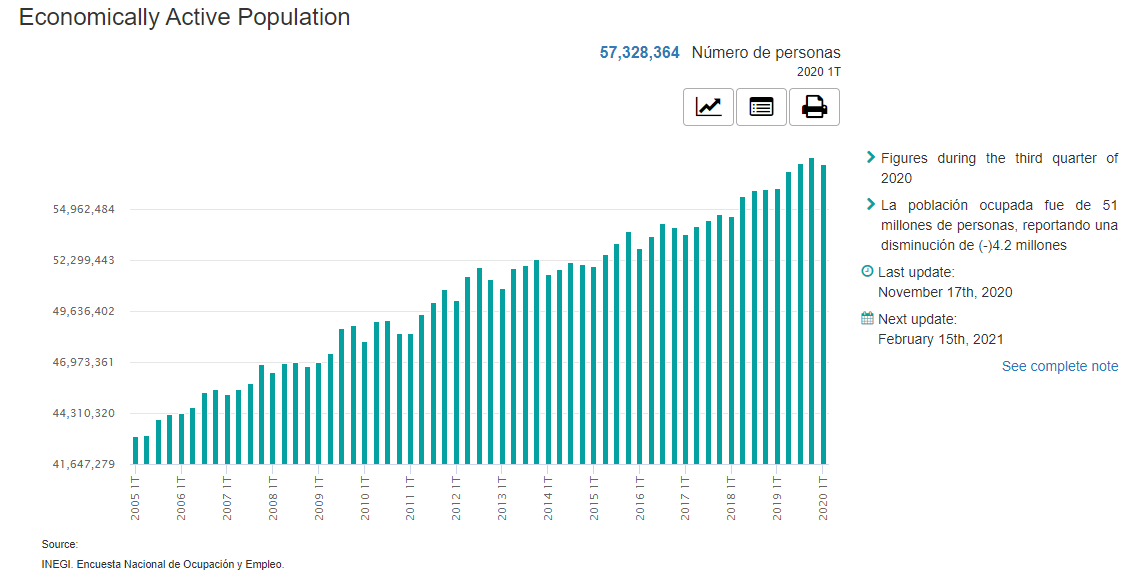
Mexico has no problem with high unemployment. Over the past 15 years, the unemployment rate ranged from 3% to 6%. The recent increase to 5,3% was due to the impact of COVID-19 on the economy.
However, it should be noted that between 2005 and 2020 the number of people employed increased from 43 million to 57,3 million. This meant that the Mexican economy was able to create new jobs and maintain a similar unemployment rate over the years. Net participation rate remained at the level of 60,3% (for the population over 15).
Debt to GDP
Compared to Latin American countries, Mexico is considered a country with a conservative fiscal policy of the government. As a result, the debt-to-GDP ratio remains moderate.
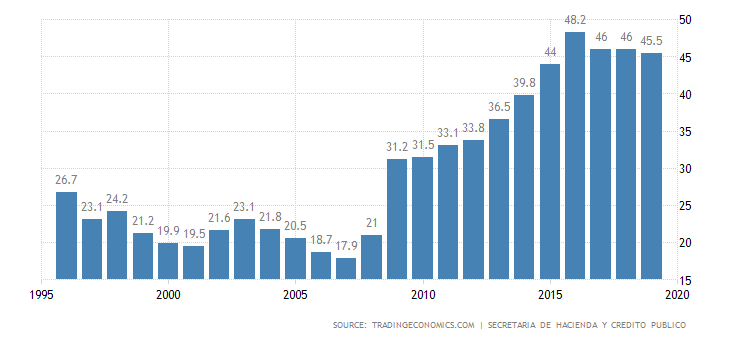 Due to the stable macroeconomic situation and moderate debt, Mexico has good ratings. The S&P agency set the rating for the government debt at BBB, while Fitch's BBB -.
Due to the stable macroeconomic situation and moderate debt, Mexico has good ratings. The S&P agency set the rating for the government debt at BBB, while Fitch's BBB -.
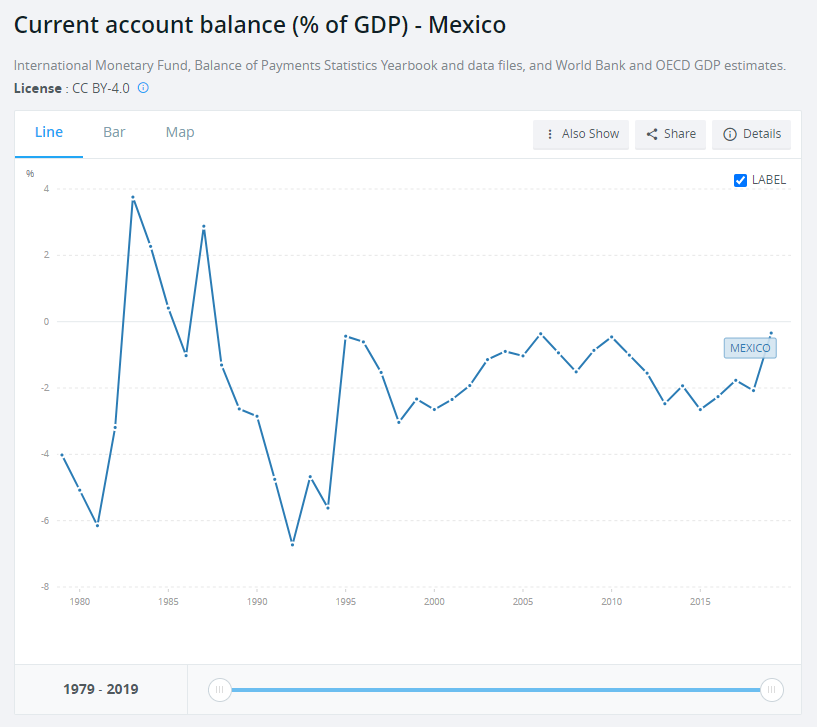
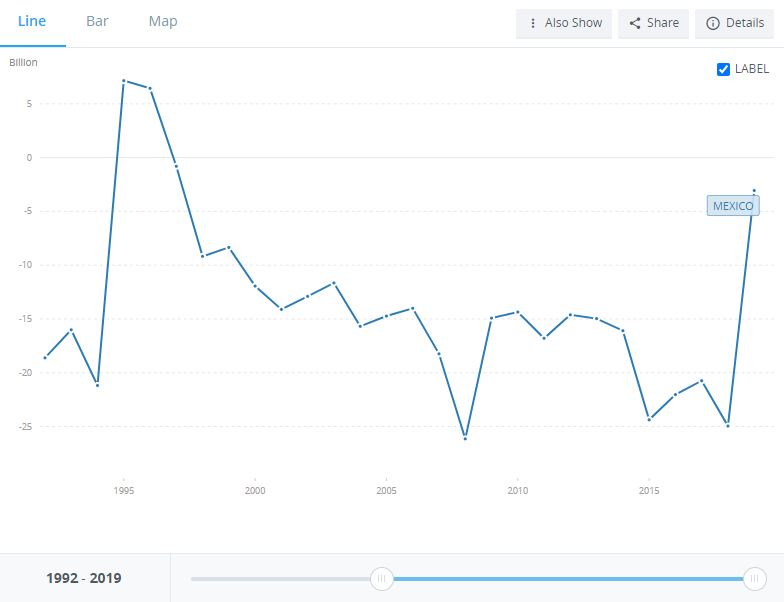
Mexico also has a current account deficit, which proves that the country is a capital importer. The higher the current account deficit, the lower the economy's resistance to external shocks (e.g. capital outflow).
Economic forecasts 2050
According to a 2017 PwC report, the Mexican economy will grow from 11th to 7th in terms of GDP after purchasing power parity. As a result, Mexico is set to surpass the economies of Germany, Japan and France in terms of size.
Banking sector
The Mexican banking sector is dominated by the "big four", which include: BBVA Bancomer, Santander Mexico, Banorte and CitiBanamex. According to data prepared by the Bank de Mexico, the "big four" had about 65% of the assets accumulated by all banks operating in Mexico (data for 2017).
World Trade
The Mexican economy is much more export oriented than the average world economy. However, the impact of exports on the economy is much smaller than in the case of Poland or Germany. Below is a comparison of selected countries:
|
Exports of goods and services as% of GDP |
1991 |
2005 |
2010 |
2019 |
|
Meksyk |
16,43% |
26,23% |
29,27% |
38,83% |
|
Germany |
23,67% |
38,06% |
42,56% |
46,97% |
|
USA |
9,66% |
10,01% |
12,32% |
11,72% |
|
Poland |
N/A |
34,61% |
40,05% |
55,75% |
|
Chile |
31,30% |
40,16% |
37,75% |
28,20% |
|
Brazylia |
8,68% |
15,24% |
10,87% |
14,32% |
|
World |
19,20% |
28,59% |
28,92% |
30,62% |
Source: World Bank
A good definition of a position on a trade map is the trade openness index, which determines the relationship between trade turnover (export and import) and a country's GDP. The higher the index, the greater the role of international trade in the country's economy. In the case of Mexico, it is clear that it is an economy much more dependent on trade than the Brazilian or Chilean economies.
|
Trade as% of GDP |
1991 |
2005 |
2010 |
2019 |
|
Meksyk |
35,79% |
53,94% |
60,76% |
77,92% |
|
Germany |
47,82% |
70,92% |
79,87% |
88,09% |
|
USA |
19,79% |
25,56% |
28,06% |
26,39% |
|
Poland |
N/A |
70,28% |
82,11% |
106,24% |
|
Chile |
58,09% |
71,62% |
69,06% |
56,76% |
|
Brazylia |
16,59% |
27,09% |
22,77% |
28,98% |
|
World |
38,53% |
56,09% |
57,03% |
60,40% |
Source: World Bank
Mexico is one of the world's largest exporters. According to data collected by the World Bank, Mexico was ranked 14th. The value of exports was estimated at $ 491,6 billion. This is more than an export from Spain or Russia. However, this is not a typical export-oriented economy. Mexico has generally experienced a trade deficit over the past 27 years.
Mexican trade continues to be concentrated in North America. The United States is by far the largest trading partner. This applies to both export and import. As a result, Mexico is very dependent on the economic health of its northern neighbor.
The exports are dominated by auto parts and cars (26%). Industrial equipment (17%) and electronic devices (17%) are next. Fuel exports amounted to 5%. It is worth mentioning that in the 80s the share of fuels in exports exceeded 60%.
Where does Mexican export go - the main partners
The largest recipients of Mexican goods are former NAFTA members. The largest share of exports goes to the United States ($ 358,7 billion). The next main directions of trade are Canada ($ 14,3 billion). It is worth noting that China is not an important export destination.
|
Place |
End |
Turnover value (billion $) |
|
1 |
United States |
358,7 |
|
2 |
Canada |
14,2 |
|
3 |
Germany |
7,1 |
|
4 |
China |
6,9 |
|
5 |
Brazylia |
4,3 |
|
6 |
Japan |
3,9 |
|
7 |
Colombia |
3,5 |
|
8 |
Great Britain |
2,8 |
|
9 |
South Korea |
2,2 |
|
10 |
The Netherlands |
2,1 |
Source: UN Comtrade
Where Mexico imports from - main partners
About 45% of imports come from the United States. This is due to with geographic proximity and with a free trade agreement. China is next, accounting for over 18% of all imports.
|
Place |
End |
Turnover value (billion $) |
|
1 |
USA |
206,1 |
|
2 |
China |
83,1 |
|
3 |
Japan |
17,9 |
|
4 |
Germany |
17,7 |
|
5 |
South Korea |
17,6 |
|
6 |
Malezja |
11,6 |
|
7 |
Canada |
9,8 |
|
8 |
Brazylia |
6,6 |
|
9 |
Włochy |
6,1 |
|
10 |
Vietnam |
6,1 |
Source: UN Comtrade
Mexico mainly imports machinery (including industrial), which accounts for around 37% of imports. Other important imported products are car parts and cars (9%) and fuels (9%).
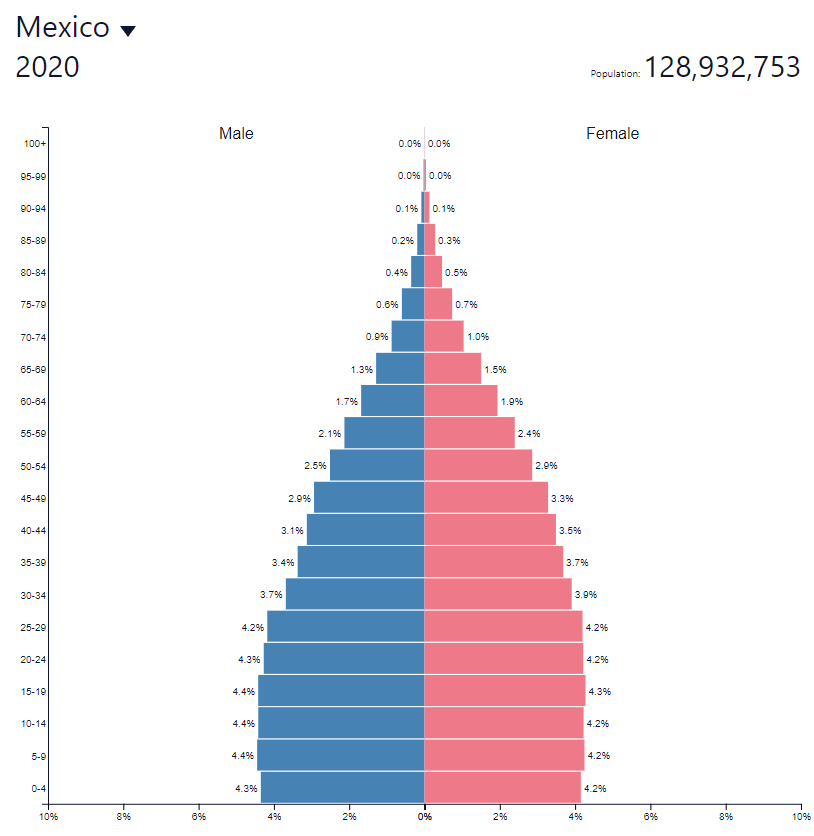
Demography - a healthy demographic structure
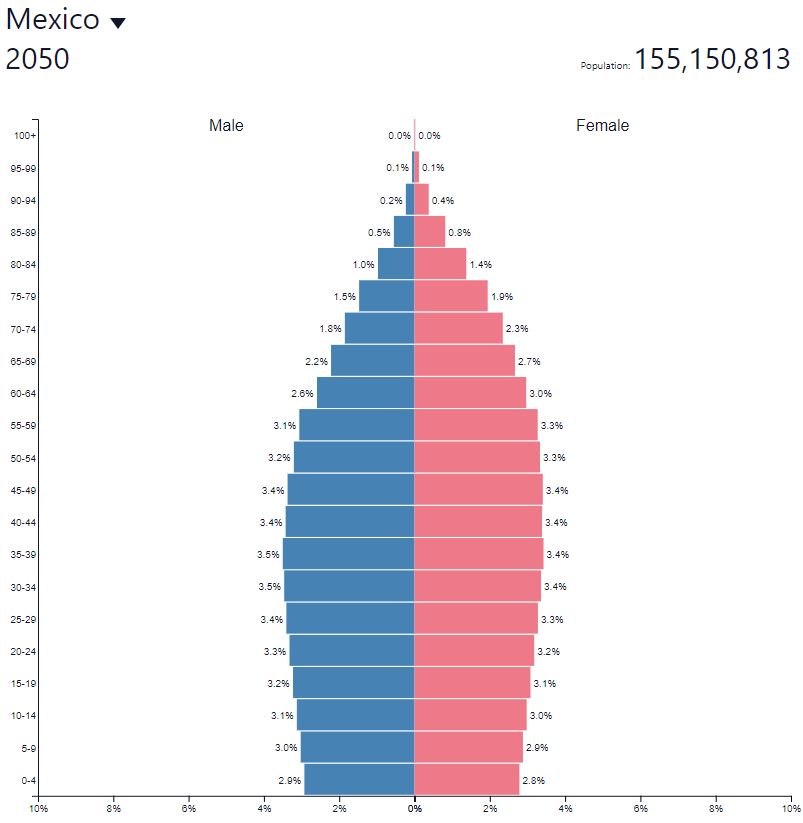
According to data from the United Nations, Mexico will have a population of approximately 2020 million by 128,9. This means that it is one of the most populous countries on earth (10th place in the world).
According to the UN, over the next 30 years Mexico's population will increase to 155,2 million. Below is a comparison with the United States and Brazil. As a result of population growth, Mexico will be able to benefit from the high proportion of the working-age population in the total population.
|
Country / Region |
2020 |
2050 |
CARG% |
|
Meksyk |
128,9 |
155,2 |
+ 0,62 % |
|
United States |
331,0 |
379,4 |
+ 0,46 % |
|
Brazylia |
212,6 |
229,0 |
+ 0,24 % |
|
World |
7 794,8 |
9 735,0 |
+ 0,74 % |
Source: UN World Population Prospects 2019
Mexico is a country with a high rate of urbanization. According to data collected by the CIA, over 80% of the population lives in cities. The largest economic center in Mexico is the country's capital - Mexico City. According to macrotrends, the city's population exceeds 21,5 million inhabitants.
The demographic structure in Mexico is very healthy. At the same time, population growth over the next 30 years will not adversely affect the Mexican pension system.
This means that no significant increase in the demographic burden is to be expected. The old dependency ratio is 11,2%. It is an indicator that divides the number of people aged over 64 by the number of people of working age (15-64). According to OECD, the ratio in Japan is over 45%.
One of the main reasons for the increase in the population is the still high TFR (Total Fertility Rate), which is over 2,12. It ensures simple replacement of generations.
Summation
Mexico is a country with one of the largest economies and population potential. The country is economically closely related to the United States, which accounts for over 70% of exports and where over 45% of imports come from.
It is a country with a stable macroeconomic situation. Mexico, however, is a developing country with significant corruption problems (according to the Corruption Perceptions Index) and a high income inequality index. The country ranks only 74th in terms of HDI. For several decades, despite the free trade agreement, there has been no convergence with the American economy (PKP PPP per capita). Despite this, the country has a large untapped potential, both economic and demographic. For this reason, it is worth having this country on the "investment radar".






















![Forex Club – Tax 9 – Settle tax on a foreign broker [Download the Application] Forex Club - Tax 9](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2024/02/Forex-Club-Podatek-9-184x120.jpg?v=1709046278)
![Trading View platform – solutions tailored to the needs of traders [Review] trading view review](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2024/03/trading-view-recenzja-184x120.jpg?v=1709558918)
![How to connect your FP Markets account to the Trading View platform [Guide] fp markets trading view](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2024/02/fp-markets-trading-view-184x120.jpg?v=1708677291)
![How to invest in ChatGPT and AI? Stocks and ETFs [Guide] how to invest in chatgpt and artificial intelligence](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2023/02/jak-inwestowac-w-chatgpt-i-sztuczna-inteligencje-184x120.jpg?v=1676364263)


![WeWork – the anatomy of the collapse of a company valued at $47 billion [WeWork, part II] wework bankruptcy story](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/wework-bankructwo-historia-184x120.jpg?v=1711729561)
![Adam Neumann – the man who screwed up Softbank [WeWork, part AND] adam neumann wework](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/adam-neumann-wework-184x120.jpg?v=1711728724)





![How to transfer shares to another brokerage office [Procedure description] how to transfer shares to another brokerage house](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2024/03/jak-przeniesc-akcje-do-innego-biura-maklerskiego-184x120.jpg?v=1709556924)

![The most common mistakes of a beginner trader - Mr Yogi [VIDEO] Scalping - The most common mistakes of a beginner trader - VIDEO](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2024/03/Scalping-Najczestsze-bledy-poczatkujacego-tradera-VIDEO-184x120.jpg?v=1711601376)
![Learning patience: No position is also a position - Mr Yogi [VIDEO] Scalping - Learning patience - No position is also a position - VIDEO](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2024/03/Scalping-Nauka-cierpliwosci-Brak-pozycji-to-tez-pozycja-VIDEO-184x120.jpg?v=1710999249)
![When to exit a position and how to minimize losses - Mr Yogi [VIDEO] Scalping - When to exit a position and how to minimize losses - VIDEO](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2024/03/Scalping-Kiedy-wyjsc-z-pozycji-i-jak-minimalizowac-straty-VIDEO-184x120.jpg?v=1710336731)


![Mexico - one of the largest economies of Latin America [part AND] mexico economy](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2021/02/meksyk-gospodarka.jpg?v=1612769864)
![Mexico - one of the largest economies of Latin America [part AND] women cryptocurrencies](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2021/02/kobiety-kryptowaluty-102x65.jpg?v=1612540783)
![Mexico - one of the largest economies of Latin America [part AND] eur / usd analysis February 2021](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2021/02/eurusd-analiza-luty-2021-102x65.jpg?v=1612772661)









