What is ROE (Return on Equity)?
The nominal value alone does not say much about the efficiency of capital allocation in the enterprise. One solution to this problem is application return on equity - ROE. ROE stands for return on equity. It means how much a given company generates profits from $ 1 of net assets. As a rule, the interpretation to say: the higher the ROE, the better the management of the company's assets is simplified. This is not entirely true. In today's text, we will present what ROE is and what its advantages and disadvantages are.
READ NECESSARY: EBIDTA - Scammers or Investors Indicator?
How to calculate ROE?
The formula for ROE is very simple. Divide the company's net profit by the value of equity. Some analysts prefer to use the value of equity for the last financial year, while others opt to calculate the average value (e.g. for the last two years or four quarters).
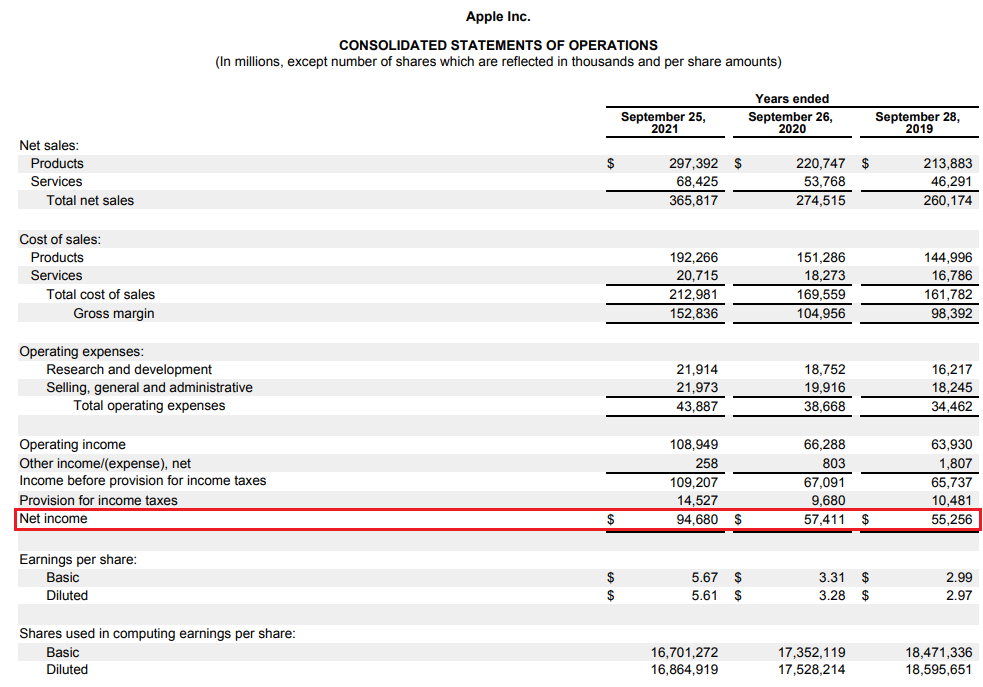
Where to get the information needed to calculate the ROE? The easiest source is to use the financial statements of the analyzed enterprise. An example would be Apple companywhich on October 29, 2021 published the financial statements for the last financial year. The first piece of information is the level of the net profit that is published in the income statement. As you can see, Apple generated a net profit of $ 2021 billion in the fiscal year ending in September 94,7.
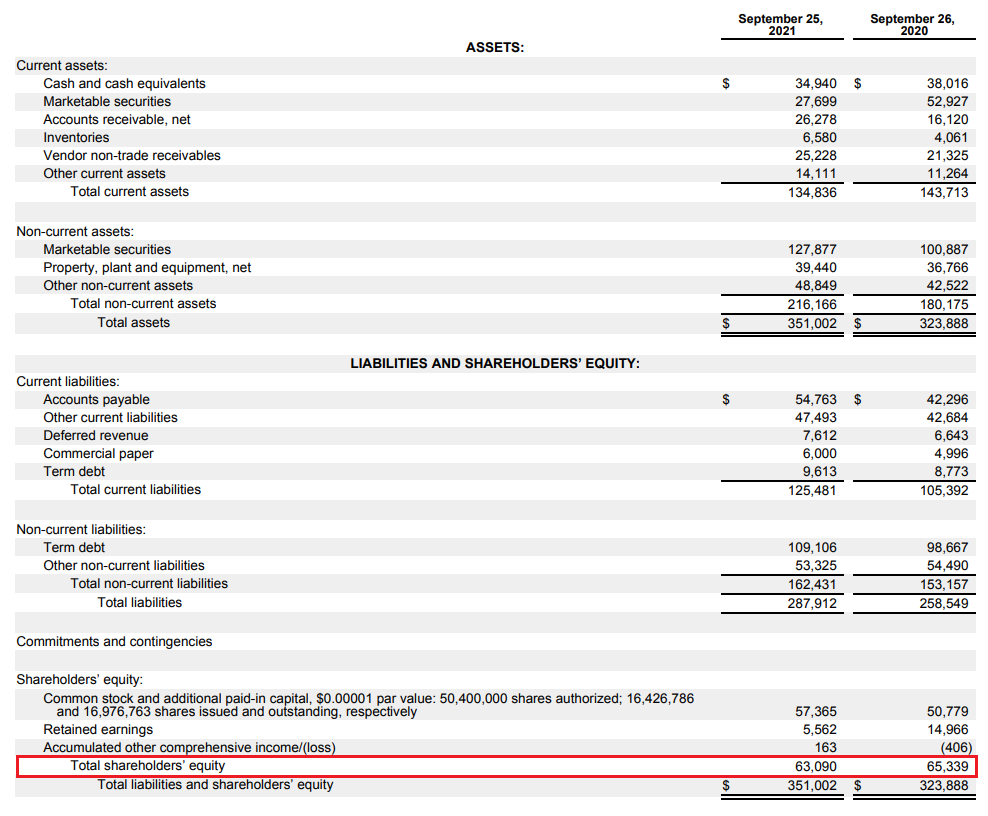
As mentioned before, the second component is the level of equity. Information on this item can be found in the balance sheet, where the company's assets and liabilities are presented. Assets are, in short, the company's assets, they include, among others inventories, receivables, cash or fixed assets of the enterprise. In turn, liabilities are a source of financing of the company's assets. In simple terms, liabilities are broken down into equity and liabilities of the enterprise. Equity means net assets, i.e. company assets reduced by the level of liabilities. Liabilities include not only interest debt but, for example, deferred revenue. These are, for example, funds received for a service that will not be delivered until the future. For Apple, deferred revenue at the end of the last fiscal year was $ 7,6 billion. The level of equity is marked in red. At the end of September 2021, the company's equity was $ 63,1 billion.
In 2021, ROE calculated using the simple method (profit from the financial year 2021 / equity at the end of the financial year 2021) was 150,07%. In turn, ROE calculated on the basis of the average equity (average from 2021 and 2020 of the financial year) amounted to 147,45%. This means that from one dollar of equity capital, the company generates one and a half dollars in net profit.
Theoretically, the higher the ROE, the more effectively the company manages its equity. However, this is only a theoretical view of ROE. In the further part of the text, we will come closer to this issue.
However, the ROE value itself can also be calculated in a different way. One of the ways is to use the so-called DuPont decomposition. This allows you to see what exactly is responsible for the ROE level. The formula for REO using DuPont's decomposition is as follows:
ROE = net profit margin * asset turnover * equity multiplier
The net profit margin is calculated by dividing the net profit by the sales revenue. It means information how many percent the company earns from one dollar of revenues. The higher the index, the higher the profitability of the products and services sold.
Asset turnover is calculated by dividing the level of sales (revenues) by assets. It is an indicator that measures the efficiency of asset management. The higher the ratio, the more assets generate more sales. Of course, the size of the asset turnover ratio depends on the conduct of business and the length of the company's operating cycle. The longer the operating cycle, the theoretically, the greater the balance sheet level. For example, a manufacturing company has to buy semi-finished products (inventories) and after the sale it often has to wait many weeks for the collection of receivables (e.g. a trade credit). Additionally, it needs factories and machines, which increases the demand for capital. In turn, the SaaS company (to put it very simply) has to "only" sell its service. He does not need to expand the factory to increase sales.
The equity multiplier is calculated by dividing assets by equity level. The higher the level of this ratio, the more assets the company finances with external capital. It can come both from the company's counterparties (e.g. trade liabilities) and e.g. from issuing bonds or taking a loan from a bank. Sometimes the indicator is negative. This is a situation where equity is negative.
How to interpret the ROE indicator
There is no single measure that can define a "normal" ROE range. It all depends on the industry in which the company operates. For this reason, it is best to compare the size of ROE with competing companies operating in the same industry. The DuPont decomposition is helpful in understanding why the return on equity has a specific value. It is worth remembering that there are several pitfalls that can distort the result. Such situations include, among others:
- Negative equity
Negative equity is a situation where an enterprise has a greater level of liabilities than assets. This means that the level of net assets (assets less liabilities) is negative. The reason for negative equity is a lot. The most obvious are the large net losses that are "covered" by debt. A negative equity alone does not mean that the company is about to go bankrupt. Sometimes negative equity is caused by the "generosity" of a company's board of directors returning more capital to shareholders than it can generate from its operations.
An example of such a company is McDonald's, which has negative equity since 2016. It resulted from a significant share buy-back and dividend payment. Due to the very good profitability and excellent capital efficiency, the company does not have to worry about conservative financial management. As a result, between 2015 and 2019, the company purchased shares worth $ 32,1 billion and paid out over $ 15 billion in dividends. During this time, the company generated $ 33 billion in operating cash flow and had to spend over $ 10 billion on CAPEX. The gap has been buried in debt. In 2016, the company's liabilities grew larger than its assets.
- One-time profit / loss
Sometimes a one-time net gain causes ROE to increase significantly. However, this does not result from the improvement of gross profitability on sales, but due to the occurrence of a situation that will be difficult to repeat. An example would be the profitable sale of a subsidiary. It is true that it generates a significant net profit, but it is not a repetitive activity. In such a situation, the net result should be "cleaned" from one-off events. Sometimes a one-off event brings losses instead of profits. An example may be penalties imposed by market regulators. An example is S&P Global, who was fined $ 2014 billion in 1,5. This resulted in a net loss of $ 115 million. A year earlier, the company generated a net profit of $ 1,4 billion. In order to calculate the "true ROE" for 2014, the net result should be removed from the one-time fine imposed on the enterprise.
- Financial leverage
The level of financial leverage has a large impact on ROE. The more a company uses external financing, the less equity it has. For this reason, if the company gets into debt aggressively, it can generate a very high ROE, which does not mean great capital management, but leverage the company. This is a dangerous policy as it increases the risk of a business falling into liquidity problems (in the absence of debt rollover). For this reason, it is also worth looking at the return on invested capital (ROIC), which better assesses the actual effectiveness of the company's capital management.
ROE, ROA, ROIC, ROCE - differences
The main difference between ROE and ROA (return on assets) is the way they calculate the management efficiency of a company. ROE focuses on net assets (less liabilities), while ROA divides net profit by the level of all assets. If the company generates a net profit and equity is greater than zero, the ROE is always greater than the return on assets.
- ROIC is short for Return on Invested Capital. Therefore, it calculates how well the enterprise allocates capital (the source of this capital is irrelevant). The denominator includes the assets that are needed to generate profits from the business. Therefore, the surplus cash is ignored. Thus, ROE looks only at the return on equity of shareholders and is sensitive to the level of leverage, while ROIC is insensitive to the level of interest debt. Another advantage of ROIC is that it deducts "excess cash". This is especially important for companies that have a large stock of cash that is kept in the account. This practice is very conservative and reduces the real profitability of the company.
- ROCE it is short for Return on Employed Capital. It is therefore an indicator "between" ROE and ROIC. ROCE focuses on return on fixed capital, which is the sum of equity and long-term debt. Return on equity should be higher than the company's cost of capital (WACC). If it is lower, it means the company is not producing shareholder value.
Summation
ROE is an indicator that allows you to determine the return on equity. Therefore, it is a measure that allows to calculate how effectively the company manages the owners' capital. The disadvantage of this indicator is its sensitivity to the amount of leverage. The more aggressively a company manages its finances (low equity in relation to assets), the ROE may be artificially high. Return on equity is an interesting measure in analyzing the effectiveness of bank capital management. Theoretically, the higher the ROE value, the more effective capital management (excluding the impact of financial leverage). However, sometimes a negative ROE is also not a bad result because it results only from the aggressive financial policy of the company (share purchases that cause equity to fall below zero). As a rule, if the company has negative equity, the ROE analysis does not make sense. Better then calculate ROIC or ROCE.






















![Forex Club – Tax 9 – Settle tax on a foreign broker [Download the Application] Forex Club - Tax 9](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2024/02/Forex-Club-Podatek-9-184x120.jpg?v=1709046278)
![Trading View platform – solutions tailored to the needs of traders [Review] trading view review](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2024/03/trading-view-recenzja-184x120.jpg?v=1709558918)
![How to connect your FP Markets account to the Trading View platform [Guide] fp markets trading view](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2024/02/fp-markets-trading-view-184x120.jpg?v=1708677291)
![How to invest in ChatGPT and AI? Stocks and ETFs [Guide] how to invest in chatgpt and artificial intelligence](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2023/02/jak-inwestowac-w-chatgpt-i-sztuczna-inteligencje-184x120.jpg?v=1676364263)


![WeWork – the anatomy of the collapse of a company valued at $47 billion [WeWork, part II] wework bankruptcy story](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/wework-bankructwo-historia-184x120.jpg?v=1711729561)
![Adam Neumann – the man who screwed up Softbank [WeWork, part AND] adam neumann wework](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/adam-neumann-wework-184x120.jpg?v=1711728724)





![How to transfer shares to another brokerage office [Procedure description] how to transfer shares to another brokerage house](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2024/03/jak-przeniesc-akcje-do-innego-biura-maklerskiego-184x120.jpg?v=1709556924)

![The most common mistakes of a beginner trader - Mr Yogi [VIDEO] Scalping - The most common mistakes of a beginner trader - VIDEO](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2024/03/Scalping-Najczestsze-bledy-poczatkujacego-tradera-VIDEO-184x120.jpg?v=1711601376)
![Learning patience: No position is also a position - Mr Yogi [VIDEO] Scalping - Learning patience - No position is also a position - VIDEO](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2024/03/Scalping-Nauka-cierpliwosci-Brak-pozycji-to-tez-pozycja-VIDEO-184x120.jpg?v=1710999249)
![When to exit a position and how to minimize losses - Mr Yogi [VIDEO] Scalping - When to exit a position and how to minimize losses - VIDEO](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2024/03/Scalping-Kiedy-wyjsc-z-pozycji-i-jak-minimalizowac-straty-VIDEO-184x120.jpg?v=1710336731)