Morgan Stanley: one of the key investment banks in the world
Most people associate investment banks with Goldman Sachs and JP Morgan. However, these are not all such entities in the world. Also the less known ones play an important role in the world of investing. One of them is Morgan Stanley. This may be an unfamiliar bank to many readers, but this institution generated over $50 billion in revenue in the last fiscal year. So it is not a small bank, but a serious institution, which certainly is TBTF (Too Big To Fail).
Morgan Stanley runs various businesses. He invests on his own account and manages the assets of his clients. In addition, he also provides assistance in financing projects or business and investment consulting. Morgan Stanley also assists in the placement (sale) of bonds or IPOs.
Over the years of operation of this one of the world's leading financial institutions, the bank has expanded its headquarters in many countries. Apart from North America, it also operates in Asia, Australia and Oceania, Africa, Europe and Latin America. It may not be surprising that the bank also has branches in China. It has a total of 4 branches in Mainland China and Taiwan (Taipei, Beijing, Shanghai and Hong Kong). In this article, we will take a closer look at the history of Morgan Stanley. This will certainly be an interesting story, because the bank is among the top XNUMX largest corporations in the United States.
The beginnings of Morgan Stanley
Morgan Stanley and JP Morgan have a similar term “Morgan”. Case? Of course not. Both banks descend from one bank: JP Morgan & Co. The reason for the separation was different views on the direction in which the institution was to develop. We have to go back to the interwar period.
Before The Great Depression it was the most important financial institution in the United States. However, 1929 changed a lot in the American economy. Not only was the investment market collapsing, but officials began to increasingly restrict American banking. Before the Great Depression, banks could conduct two businesses at the same time. This caused the stock market crash to contribute to the insolvency of some of them and sow uncertainty among customers. Bank runs began (requests from a large number of customers for refunds). The bank run, combined with the fractional reserve system, was a death sentence for many institutions. After the situation in the banking sector calmed down, it was decided to fight against the current practice. By virtue of Glass-Steagall Act it was no longer possible for an investment bank to also carry out normal banking activities, where the normal banking activities are to collect deposits from customers and grant loans.

Henry S. Morgan. Source: wikipedia.org
JP Morgan & Co. faced with a choice: to focus on the investment activity, which is experiencing a huge collapse, or to fight in the commercial banking sector. After heated discussions, it was decided to go into commercial activity. Not all bank employees liked it. As a result, many of them, including such important figures as Henry S. Morgan and Harold Stanley, decided to leave the company. Together with Drexel, they created Morgan Stanley. This took place in 1935. This year is considered to be the beginning of the history of this institution.
The market was very difficult at the beginning. Many companies were licking their wounds after the massive depression that hit the American economy. Interest in investing in the capital market has also decreased significantly. However, thanks to its network of contacts and its own experience, Morgan Stanley quickly gained significant market shares. In its first year of operation, Morgan Stanley had approximately 24% of the IPO market share. Morgan Stanley assisted in public offerings worth $1,1 billion.
As it turned out, this was only the beginning of his development. With each quarter, Morgan Stanley increased its importance in the market. The more transactions the bank participated in, the easier it was for it to get new orders. One example is the 1938 transaction. then this Morgan Stanley was a major bond dealer United Steel Corporation worth $100 million. The name United Steel doesn't make much of an impression today, but back then it was one of the most important companies in the United States. Such a contract was a distinction for the only 3-year-old Morgan Stanley. It is therefore not surprising that the bank managed to become the main advisor to railroads in the United States. At that time, railroads were one of the most important sectors of the American capital market.
At the turn of 1941 and 1942, Morgan Stanley became a member of the NYSE, i.e. the New York Stock Exchange. Thanks to this, he could place orders directly on the local trading floor. This allowed it to expand its offer for its customers. Japan's attack on the USA caused the capital market to slow down its development again. However, Morgan Stanley continued to steadily build its reputation. As it turned out later, it paid off in the future. It is worth remembering that in the 40s the bank began its charitable activities. The pioneer was Harold Stanley, who spent $1,5 million to help European children.
Post-war period

Harold Stanley. Source: wikipedia.org
After the end of World War II, great prospects began for Morgan Stanley. Europe needed capital to rebuild from war damage. This, in turn, was an opportunity for American companies. In order to develop their business, they needed additional capital. Morgan Stanley became an advisor to many of the American companies that took part in rebuilding the economic potential of Europe. Countries and international institutions were also involved in the economic reconstruction. As an example can be given world Bank. Morgan Stanley participated in the issue of bonds of this institution. The funds were to be used for the reconstruction of post-war Europe. Cooperation with the World Bank was also continued in the following years.
Years of development on the capital market allowed us to build relationships that paid dividends in the 50s. As a result, the bank helped issue General Motors bonds (amount of $300 million), IBM shares ($230 million) and AT&T ($250 million).
It is worth noting that in the early 50s, there was a change in the position of CEO of Morgan Stanley. At that time, he resigned Harold Stanley. His place was taken by Parry Hall. He held this position until 1971. It was a big change. Harold Stanley was one of the founders and first president of Morgan Stanley. A change in position also emphasizes new directions of development. This was necessary as the world was entering the world of computers. Slowly, this revolution also affected finances.
1960 – 1979: Geographic expansion and business transformation
In the 60s, computers ceased to be built only in military units, universities or laboratories. They also began to reach financial institutions. Thanks to them, it was possible to carry out computational operations on an unprecedented scale. At that time, there was a significant information asymmetry between large financial institutions and ordinary investors. It was the golden age of many simple investment strategies. It was then that Morgan Stanley was testing computer systems for taking trades in the market and creating software to aid in increasingly sophisticated financial analysis.
The end of the 60s was also a time of geographical expansion. Along with the tightening of cooperation between the USA and Western Europe, American banks tried to gain shares in the European capital market. To facilitate business in Europe, in 1967 the first foreign branch was established. An office was opened in Paris. Interestingly, after 10 years the bank moved its branch to London. It can be assumed that the reason for this decision was that London was the largest financial center in Europe and was a member of the European Union (since 1973). Moreover, language issues certainly helped.
The bank was not just looking at Europe. Already in 1970, an office was opened in Japan. Japan in those days was what China was in 2010. A country that is developing dynamically and taking over new markets. The dynamic development of Japan was an opportunity for great profits in the Land of the Rising Sun. That is why Morgan Stanley wanted to take advantage of the huge potential of that capital market.
The turn of the 70s and 80s also saw the expansion of the bank's activities. There was also a reorganization of Morgan's operations to increase operational efficiency. Departments responsible for wealth management, asset management and real estate investments appeared.
1980 – 2007: The golden age of banking
In 1984, the bank created a data processing system called TAPS (Trading Analysis Processing System). As a result, its operational efficiency increased. However, Morgan Stanley focused only on its investment activities. In 1986, he bought part of the rights to the indices belonging to Capital International. After this transaction, he changed the name of his product to Morgan Stanley Capital International (MSCI). After only three years, the MSCI indices were the most important benchmarks for markets outside the US. In 1988, Morgan Stanley created the first index for developing markets. To this day, it is one of the most important benchmarks for funds and ETFs investing in developing countries.
Currently, MSCI is one of the largest providers of indices in the world (together with S&P Dow Jones Indices and FTSE). It wasn't until 2007 that Morgan Stanley decided to divest part of its stake in MSCI in the company's initial public offering. As it turned out, that wasn't a good idea. MSCI has increased over 2200% since its debut. At the same time, Morgan Stanley shares by only 100%. As you can see, this American investment bank did not always have good investment ideas.
The end of the 80s saw the enthusiasm for globalization. This trend also affected Morgan. Offices and branches were opened in many places around the world. Asia was particularly successful, as it already had great prospects.
The 90s were the triumph of the Washington consensus. The opening of the Eastern Bloc economies to the world was another factor supporting the expansion of American banks. Another factor supporting the development of financial markets was the technological boom. Bubble in the dotcom market supported the IPO market as well as mergers and acquisitions. This kept Morgan Stanley's hands full. However, the years 2000-2003 were very difficult for the capital market. The reason was the bank burst on the markets of technology companies and the attack on the World Trade Center. In the attack of September 11, 2001, 13 workers lost their lives as a result of the attack. One of them was Rick Rescorla, who, as security director, was responsible for evacuating employees from buildings at risk.
Following the easing of monetary policy by FED and the widespread use of derivatives (including MBSs, CDOs, CDS or swaps), strong growth began on the American real estate market. The profits from derivative transactions were very large. At the same time, there was a belief that thanks to advanced risk control models, very high financial leverage could be used. It ended in a tragedy that cost American society a lot.
Crisis in the company and its negative consequences
In 2005, a problem arose within the investment bank itself. Philip Purcell was the CEO of Morgan Stanley at the time and had a different responsibility about the investment bank's policy from some managers and shareholders. Purcell was against increasing financial leverage and investing in derivatives related to the US subprime market. He believed that this was a departure from the bank's tradition and could expose it to large losses in the future. On the other hand, some management and investors believed that Morgan Stanley was losing market and talent. The beginning of 2005 saw a small exodus of employees of this investment bank. This was due to the competition paying more. For this reason, supporters "dancing while the music plays" they believed that this was the only way Morgan Stanley would regain market share and protect the company from talent drain.
In the end, the option won out "dance" instead "of reason". As a result, the CEO resigned, and the bank began to act aggressively in new markets. The reason for this strategy was the desire to quickly make up for lost time. This aggressive policy later backfired. You could say that ultimately Philip Purcell was right. Only because he was not the bank's CEO, he could only watch the problems that were inevitable.
Morgan Stanley after the 2007/2008 crisis
In the years 2007-2008, a slow erosion of the value of assets continued “a promising market for derivatives based on subprime assets”. Even in early 2008, the bank kept its cool as it advised the US government in bailing out Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac. However, in early September 2008, Morgan Stanley himself needed financial assistance. During the crisis in the American real estate market the share price of this American investment bank fell by more than 80%. It was an investment opportunity for many market participants who had capital. One of the investors was the Japanese MUFG Bank, which paid PLN 21 billion for 9% of the company's shares. However, in addition to investor help, government support was necessary. Morgan Stanley, along with seven other US banks, received investments from the TARP bailout program.
The company continued to develop in the following years. The low interest rate policy helped support the boom in stock markets. As a result, revenues from investment consulting, asset management and proprietary trading increased. It's no surprise that the company's revenues were growing in the years before COVID-19. Currently, the company finds itself in a difficult market environment. High inflation, tightening monetary policy and economic slowdown are not helpful.
It is worth mentioning that the bank is constantly up to date with new trends. In 2012, Morgan Stanley launched a solution that allows you to match customer portfolios to ESG scoring. As you can see, more than a decade ago, Morgan Stanley became interested in sustainable activities.
Shortcuts: ESG-based investing is about selecting companies that meet environmental, social and corporate criteria (i.e. maintaining corporate governance).
The next step that matched the current trends was Inclusive Ventures Group, which was created by Morgan Stanley in 2017. As the name suggests, the fund wants to create a more "inclusive" investment world. For this reason, the fund focuses on investing in projects created by more inequalities (including racial inequalities) in American society.
In 2020, the bank took over for $13 billion e-trade. This allowed us to increase the scale of our activities in the field of property management and asset management. An additional advantage was the acquisition of a brokerage business, which provides the opportunity for further diversification.
In 2009, Morgan Stanley acquired from Citigroup Smith Barney. A subsidiary named Morgan Stanley Smith Barney was formed. It is one of the largest asset management companies in the world. Its assets in 2014 were estimated at over $2 trillion (i.e. $2000 billion). Interestingly, Morgan Stanley paid over $5 billion for Smith Barney.
Morgan Stanley scandals
Like many investment banks, Morgan Stanley also occasionally receives fines for violating regulations. Most of the penalties received by the bank were small for the scale of this institution. However, sometimes the fines received ran into the billions of dollars. One example is a 2014 settlement that was signed by Morgan Stanley with the FHFA (Federal Housing Finance Agency). By agreement the bank agreed to pay a $1,25 billion fine for unethical activities before the subprime crisis. As a result of the fraud, government institutions such as Fannie and Freddie had to be bailed out by the government to keep them from going bankrupt. However, it wasn't the only punishment related to the real estate market. In 2016, the Department of Justice announced that it had reached an agreement with Morgan on the matter to pay a $2,6 billion fine for defrauding investors. The problem was the fact that Morgan Stanley did not inform clients that some MBSs are based on assets of very poor quality. The case concerned the sale of RMBSs, i.e Residential Mortgage-Backed Securities. These were derivatives based on real estate loans.
Current activity of the bank
Morgan Stanley is one of the components the S&P 500 index. The company's current capitalization exceeds $140 billion. In 2022, the company's revenues amounted to $50,2 billion, while net profit amounted to $11 billion that year.
It is worth noting that Morgan Stanley is one of the leaders in the global asset management market.

Source: Morgan Stanley
Over the past 12 years, revenue has grown from $32 billion to $54 billion. At the same time, along with the increase in the scale of operations, the companies managed to increase the profitability of ROTCE (Return on Tangible Common Equity). This profitability ratio has increased from 10% in 2010 to 16% in 2022.
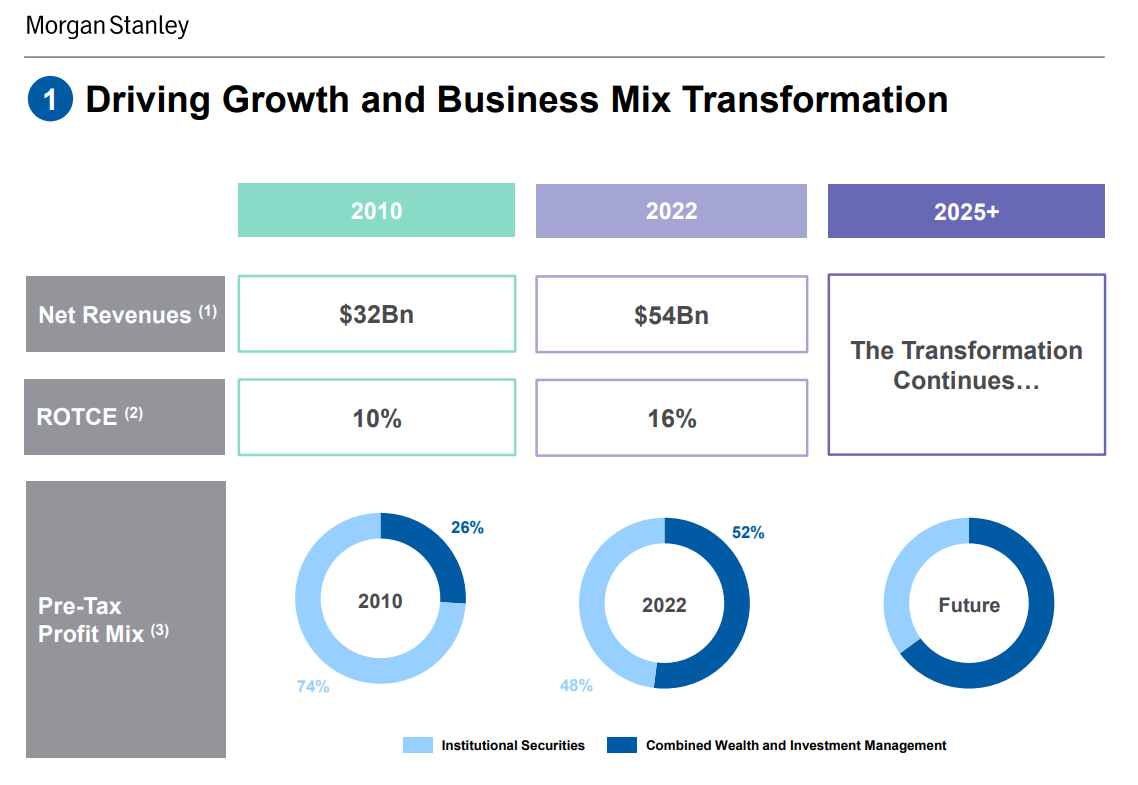
Source: Morgan Stanley
The gross margin in the asset management segment increased significantly. In 2009, the gross margin was 14%. For 6 years, Morgan Stanley has been building scale, which will allow it to increase the margins of its segment in the future.
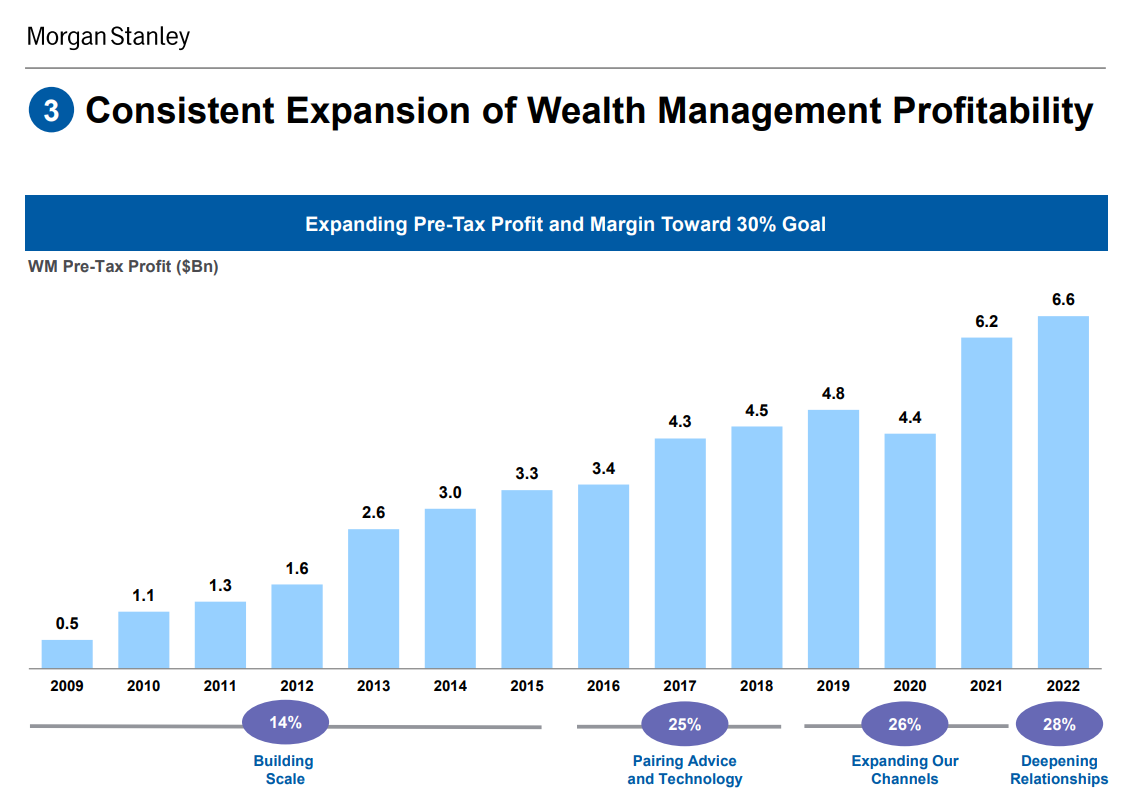
Source: Morgan Stanley
In 2022, this American bank transferred billions of dollars of capital to investors in the form of dividends and share buybacks. The purchase value was estimated at approximately 9% of the capitalization value. In the coming years, a continuation of the share buyback and dividend payment can be expected. Thus, Morgan Stanley is a typical category company dividend growth.
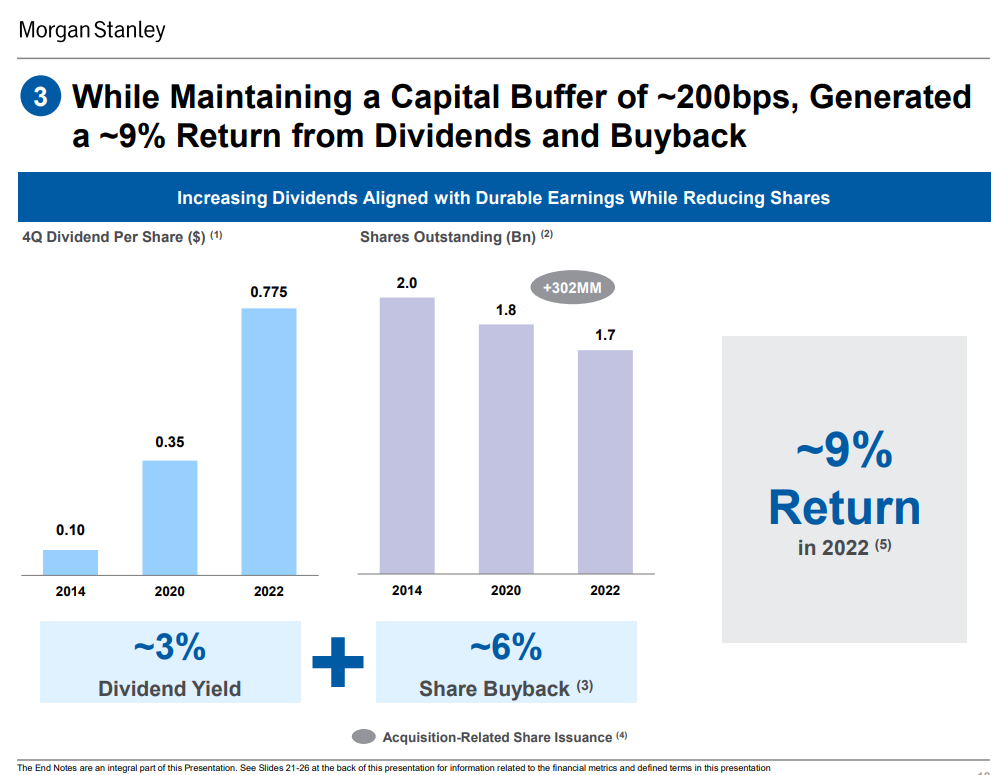
Source: Morgan Stanley
The company intends to continue to develop. This can be seen in the chart below. The Bank expects that thanks to the inflow of capital to investment activities and the organic growth in the volume of assets resulting from profitable investments, the profit before tax of this segment is to double in the long term.
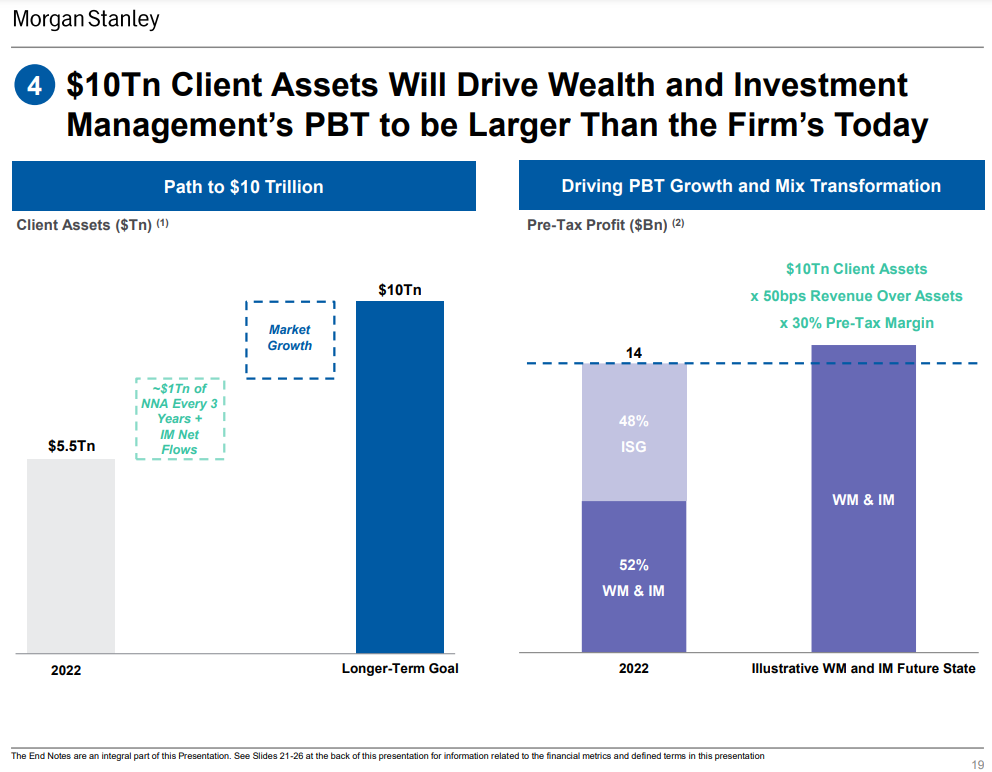
Source: Morgan Stanley
It also shows its investors its long-term goals. Morgan Stanley will want to raise net $3 billion from clients every three years. The long-term goal is to have a $1 trillion asset and wealth management segment. At the same time, the increase in the scale of operations is expected to improve the ROTCE profitability index, which is expected to amount to 10%.

Source: Morgan Stanley
Summation
Morgan Stanley is one of the largest investment banks in the world. The bank has almost 90 years of history full of ups and downs. However, despite the failures, the bank was able to develop new branches of activity. It was thanks to Morgan Stanley that MSCI, which is one of the largest providers of indexes in the world, became widespread. The bank is one of the key institutions on the capital market and investment banking. MS is even listed on the Warsaw Stock Exchange, which is one of the insignificant places for trading shares. MS on the podium in the stock market traded. In December 2022, MS on this market amounted to over 10%, which allowed this investment bank to take 2nd position in terms of turnover.
Morgan Stanley is certainly an interesting example of an American investment bank that has proven itself over many years "indestructibility". The development was not hindered by wars or the collapse of the monetary system (Bretton Woods) or deep bear markets. It is worth noting that the company is very eager to share its long-term strategy with investors. We'll see if they do in the future






















![Forex Club – Tax 9 – Settle tax on a foreign broker [Download the Application] Forex Club - Tax 9](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2024/02/Forex-Club-Podatek-9-184x120.jpg?v=1709046278)
![Trading View platform – solutions tailored to the needs of traders [Review] trading view review](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2024/03/trading-view-recenzja-184x120.jpg?v=1709558918)
![How to connect your FP Markets account to the Trading View platform [Guide] fp markets trading view](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2024/02/fp-markets-trading-view-184x120.jpg?v=1708677291)
![CRB index – one of the popular commodity market benchmarks [Guide] crb index](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2024/05/indeks-crb-184x120.jpg?v=1715055656)
![How to invest in ChatGPT and AI? Stocks and ETFs [Guide] how to invest in chatgpt and artificial intelligence](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2023/02/jak-inwestowac-w-chatgpt-i-sztuczna-inteligencje-184x120.jpg?v=1676364263)






![Izabela Górecka – “Success on the market depends not only on knowledge, but also on emotional stability” [Interview] Izabela Górecka - interview](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/Izabela-Gorecka-wywiad-184x120.jpg?v=1713870578)
![WeWork – the anatomy of the collapse of a company valued at $47 billion [WeWork, part II] wework bankruptcy story](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/wework-bankructwo-historia-184x120.jpg?v=1711729561)
![Adam Neumann – the man who screwed up Softbank [WeWork, part AND] adam neumann wework](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/adam-neumann-wework-184x120.jpg?v=1711728724)

![The most common mistakes of a beginner trader - Mr Yogi [VIDEO] Scalping - The most common mistakes of a beginner trader - VIDEO](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2024/03/Scalping-Najczestsze-bledy-poczatkujacego-tradera-VIDEO-184x120.jpg?v=1711601376)
![Learning patience: No position is also a position - Mr Yogi [VIDEO] Scalping - Learning patience - No position is also a position - VIDEO](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2024/03/Scalping-Nauka-cierpliwosci-Brak-pozycji-to-tez-pozycja-VIDEO-184x120.jpg?v=1710999249)
![When to exit a position and how to minimize losses - Mr Yogi [VIDEO] Scalping - When to exit a position and how to minimize losses - VIDEO](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2024/03/Scalping-Kiedy-wyjsc-z-pozycji-i-jak-minimalizowac-straty-VIDEO-184x120.jpg?v=1710336731)


















