Return On Capital Employed (ROCE) - an indicator measuring the operational efficiency of a company
Ultimately, every fundamental analyst must ask himself: does the company allocate its capital in a good way? The future ability to generate value for the company's owners depends on the proper management of the company's funds. Of course, there are many ways to calculate the effectiveness of enterprise asset management. These include: ROA, ROE, ROIC and ROCE. Each indicator has its advantages and disadvantages. Today we will focus on the analysis of the last of them. ROCE can be a useful tool for analyzing many companies.
How to calculate ROCE?
ROCE is different Return On Capital Employed, i.e. profitability of invested capital. The indicator is to measure the effectiveness of the capital used. In other words, the indicator allows you to assess how much profit a given company can generate from the capital invested by the company. ROCE is used by financial managers, shareholders, investors and investment analysts.
ROCE is calculated by dividing the operating profit by the constant capital. Operating profit is a measure of the effectiveness of an enterprise's operating activities. It is profit before taxes and the impact of financial costs and revenues. It is therefore a basic measure that shows how healthy the operational activity of the enterprise is. Contrary to ROIC, NOPAT (operating profit after tax) is not calculated, but operating profit itself. As a result, ROCE is not sensitive to differences in tax rates, which enables easier comparison of companies from the same industry but operating in other countries.
Constant capital, on the other hand, is a measure that is calculated by adding equity to long-term liabilities. Constant capital is therefore an indicator that takes into account some of the company's liabilities. Fixed capital can be calculated in many ways. Some analysts prefer to use the value of the constant capital for the last financial year, while others opt to calculate the average value (e.g. for the last two years or four quarters). Another difference is how long-term liabilities are calculated. Some analysts prefer to include all long-term liabilities in their fixed capital, while others only use interest on long-term liabilities (e.g. credits and loans) for their calculations.
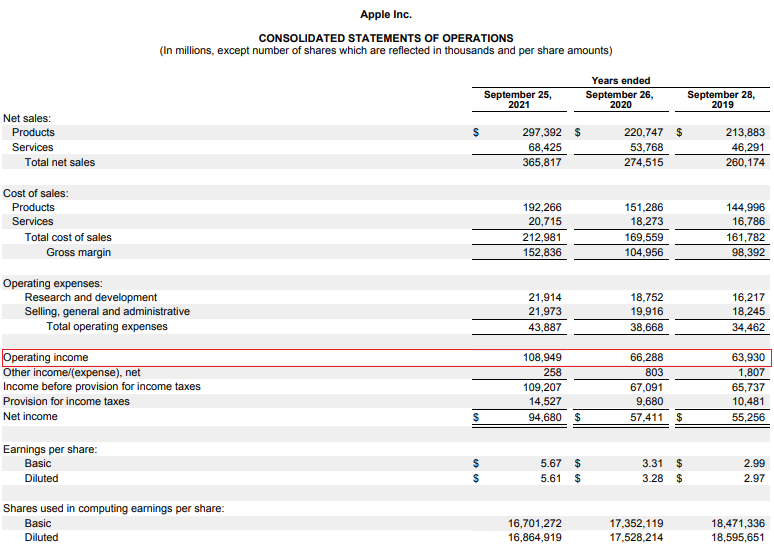
Where to get the information needed to calculate the ROCE? The easiest source is to consult companies' published financial statements. The easiest access is to listed companies that are required to publish annual and periodic financial reports. As you can see, Apple Lossless Audio CODEC (ALAC), generated $ 2021 billion in operating profit in the fiscal year ending September 108,95.
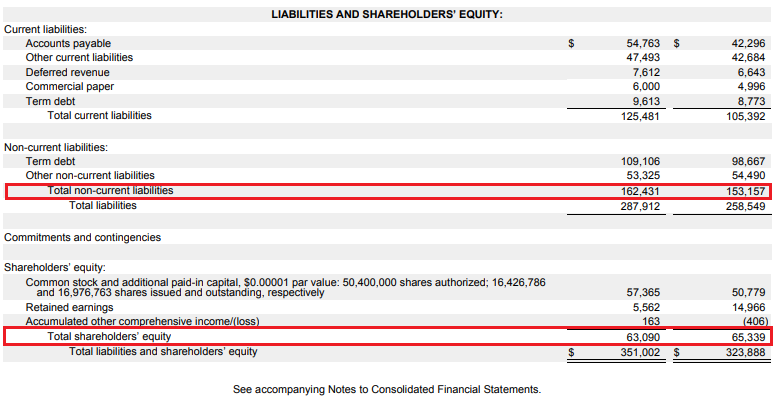
As mentioned before, the second component is constant capital level. Information on this item can be found in the balance sheet, where the company's assets and liabilities are presented. Assets are, in short, the company's assets, they include, among others inventories, receivables, cash or fixed assets of the enterprise. In turn, liabilities are a source of financing of the company's assets. In simple terms, liabilities are divided into equity and liabilities of the company. Equity means net assets, i.e. company assets reduced by the level of liabilities. On the other hand, long-term liabilities include interest liabilities or deferred revenue. These are, for example, funds received for a service that will not be delivered until the future.
The level of equity is marked in red. At the end of September 2021, the company's equity was $ 63,1 billion. The long-term liabilities at the end of the financial year amounted to $ 162,4 billion.
In 2021, ROCE calculated using the simple method (profit from the financial year 2021 / fixed capital at the end of the financial year 2021) was 48,31%. In turn, ROCE calculated on the basis of the average equity (average from 2021 and 2020 financial years) amounted to 49,07%. This means that from one dollar of equity capital, the company generates one and a half dollars in net profit.
Theoretically, the higher the ROCE ratio, the more effectively the company manages its fixed capital. However, this is only a "book" look at the ROCE indicator. In the further part of the text, we will come closer to this issue.
Return On Capital Employed - interpretation
ROCE informs the analyst how much operating profit is generated by one unit of equity. Therefore, it is an indicator that determines the operational efficiency of an enterprise. Every company should focus on creating shareholder value. The higher the ROCE value, the better the company uses its capital. It is also worth looking at the trend of the ROCE indicator. If the level of the ratio deteriorates with each analyzed period, this is a message for the management board that it is necessary to look at the latest investments in the company and the profitability of individual product groups.
Return On Capital Employed it can also be used as an indicator of comparing the company with the competitive environment. If the ratio of the audited company is lower than that of the closest competitors, it may mean that the management board of the audited company should implement a recovery plan to increase operational efficiency.
ROCE can also be interpreted in relation to the value of the weighted average cost of capital (WACC). If the ROCE is higher than the WACC, it means that the company's activities create value for shareholders. In such a situation, the company should look for the possibility of reinvesting the surplus cash in the business again. However, if the ROCE is lower than the WACC, then the focus should be on improving profitability or restructuring the business (sale of ineffective production plants, etc.). Of course, in the case of fast-growing companies, the ROCE index may not be an appropriate measure. This is due to the fact that many companies that are in the phase of dynamic growth focus on the ratio of CAC (acquisition cost) to LTV (value of acquired customer).
There is no single measure that allows a "normal" ROCE range to be defined. It all depends on the industry in which the company operates. For this reason, it is best to compare the size of ROCE with competing companies operating in the same industry. The DuPont decomposition is helpful in understanding why the return on equity has a specific value. It is worth remembering that there are several pitfalls that can distort the result. Such situations include, among others:
- Manipulating the result
ROCE takes into account accounting results, which means that it is susceptible to various manipulations in the books. One of them may be the capitalization of costs, which may improve the result in fast-growing companies. Cost capitalization consists in recognizing a part of expenses (e.g. R&D) in fixed assets and then amortizing them over a period of e.g. 3 years.
- Accounting rules
Another example is how companies recognize revenue. An example would be alteryxwhich, when using ASC 606, recognized 35-40% of the value of a multi-year contract "in advance". As a result, signing new contracts increased the rate of revenue growth stronger than it was in the case of recognizing the contract "linearly".
- Cyclical companies
Such companies can achieve very good results in good times. During this period, the company can achieve very high ROCE levels. However, when the boom in the cyclical industry wears off, ROCE drops significantly and even becomes negative. Please note that ROCE is not a forecast tool and it cannot be used to predict future profitability for cyclical companies. For example, oil producing companies (Exxon, Chevron) achieved a negative ROCE in 2020 due to very low hydrocarbon prices.
ROE, ROA, ROIC, ROCE - differences
One of the most popular capital efficiency ratios is ROE. ROE stands for return on equity. It is calculated by dividing the net result by the level of equity. This type of ratio is sensitive to the level of leverage. The higher the debt of the enterprise, the greater the chance of achieving high return on equity.
ROA it is calculated by dividing the net profit by the entire assets of the enterprise. For this reason, the ratio is insensitive to financial leverage, but it does not effectively measure the effectiveness of wealth management. The disadvantage of the index is that the denominator counts "productive assets" as well as property that is not needed for operating activities (eg land, surplus cash or cash equivalents).
ROIC it is the index closest to ROCE. However, NOPAT (Operating Profit After Tax) is used in ROIC instead of operating profit. ROIC is also more restrictive in calculating actual invested capital than ROCE. For example, ROIC deducts "excess cash" from invested capital.
Summation
Return On Capital Employed is a useful metric to measure the effectiveness of a company's capital management. It is also a useful measure to compare the analyzed company with the competition. Theoretically, the higher the ROCE value, the more effective capital management of the enterprise. In its structure, it is similar to ROIC, because operating profit is included in the numerator instead of net profit. Unlike ROIC, ROCE does not deduct taxes from operating profit. The denominator of the ROCE is fixed capital (equity + long-term liabilities) and the invested capital in ROIC.






















![Forex Club – Tax 9 – Settle tax on a foreign broker [Download the Application] Forex Club - Tax 9](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2024/02/Forex-Club-Podatek-9-184x120.jpg?v=1709046278)
![Trading View platform – solutions tailored to the needs of traders [Review] trading view review](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2024/03/trading-view-recenzja-184x120.jpg?v=1709558918)
![How to connect your FP Markets account to the Trading View platform [Guide] fp markets trading view](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2024/02/fp-markets-trading-view-184x120.jpg?v=1708677291)
![How to invest in ChatGPT and AI? Stocks and ETFs [Guide] how to invest in chatgpt and artificial intelligence](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2023/02/jak-inwestowac-w-chatgpt-i-sztuczna-inteligencje-184x120.jpg?v=1676364263)


![WeWork – the anatomy of the collapse of a company valued at $47 billion [WeWork, part II] wework bankruptcy story](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/wework-bankructwo-historia-184x120.jpg?v=1711729561)
![Adam Neumann – the man who screwed up Softbank [WeWork, part AND] adam neumann wework](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/adam-neumann-wework-184x120.jpg?v=1711728724)





![How to transfer shares to another brokerage office [Procedure description] how to transfer shares to another brokerage house](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2024/03/jak-przeniesc-akcje-do-innego-biura-maklerskiego-184x120.jpg?v=1709556924)

![The most common mistakes of a beginner trader - Mr Yogi [VIDEO] Scalping - The most common mistakes of a beginner trader - VIDEO](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2024/03/Scalping-Najczestsze-bledy-poczatkujacego-tradera-VIDEO-184x120.jpg?v=1711601376)
![Learning patience: No position is also a position - Mr Yogi [VIDEO] Scalping - Learning patience - No position is also a position - VIDEO](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2024/03/Scalping-Nauka-cierpliwosci-Brak-pozycji-to-tez-pozycja-VIDEO-184x120.jpg?v=1710999249)
![When to exit a position and how to minimize losses - Mr Yogi [VIDEO] Scalping - When to exit a position and how to minimize losses - VIDEO](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2024/03/Scalping-Kiedy-wyjsc-z-pozycji-i-jak-minimalizowac-straty-VIDEO-184x120.jpg?v=1710336731)