Collar strategy - cheap wallet security
An option can be a great instrument to help you manage your investment portfolio. One of the interesting investment strategies is the collar, which can be used as a way to effectively hedge your stock portfolio against declines. Interestingly, talking about this strategy was one of the covers for Bernard Madoff to the financial pyramid he created. In today's article you will find answers to the following questions:
- How does the collar strategy work?
- When to use the collar strategy?
- How is the collar different from the bull's spread?
- What is a non-cost collar?
- How to manage a collar?
How does the collar strategy work?
The strategy is used by investors who wish to hedge a portfolio of stocks. In order to protect against declines, the investor purchases a put option (usually OTM) and issues a call option (also OTM) to reduce the costs of buying a put option. So it is a combination of protective put (actions + long put) and covered call (actions + short call) strategies.
The collar strategy can be created by:
- simultaneous writing of a call option and purchase of a put option
- management of the protective put strategy
- optimization of the covered call strategy
The best scenario for creating a collar is an increase in the share price to the level of the written call option. Then the maximum profit from the strategy is achieved. Too large an increase in the rate causes the investor to lose the chance for additional profits from a long position on the underlying instrument, as the profits are "eaten" by the issued call options.
Why might an investor be interested in creating a collar?
- securing your earnings from a long position in stocks
Let's deal with the first case, i.e. securing your profits from a long position in stocks. In this situation, the investor is afraid that there may be a correction in the market in the near future. At the same time, he does not want to sell his shares because he is interested in holding them for many quarters or even years. For this reason, I am looking for a strategy that offers a chance for slight increases in the value of the equity portfolio in the event of slight increases and securing most of the profits against temporary drops..
An example would be an investment in Apple shares. In June 2022, the investor purchased 300 shares of this company at an average price of $ 130. In mid-August 18, the company's share price rose to $ 174,5. The investor still wants to be a shareholder in Apple, but fears a correction. To hedge his position, he bought 3 put options with an exercise price of $ 170 and expiring on December 16, 2022. The cost of one option was $ 9,25 (per share), or the total cost of hedging was $ 2775. This means that you were hedging your portfolio from falling below $ 160,75.
The buyer of the put option decided to reduce its cost of the hedging strategy. To this end, he issued 3 call options on the same day with an exercise price of $ 180. He received $ 9,56 per share for it. This meant that the strategy was cost-free. The investor even received $ 93 [i.e. ($ 9,56 - $ 9,25) * 300].
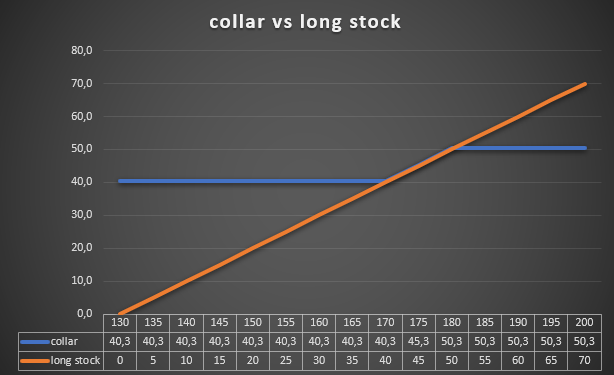
Source: own study
As you can see, the collar strategy secures profits at the level of $ 40,31 per share, i.e. at the level of $ 12 (excluding transaction costs). Meanwhile, the maximum profit is $ 093 per share. The maximum profit will take place when the Apple price rises to $ 50,31 (180% compared to the rate on August 3,15). The collar strategy will be a burden for the investor's portfolio only in the case of the scenario when by December 18, 16, the Apple share price rises above $ 2022.
- improving the profitability of the protective put strategy after the share price rises
A protective put is the simplest protection strategy. It involves the purchase of a put option, which is to protect the stock portfolio against a sudden loss of value. However, it is sometimes possible to improve the profitability of this strategy. Only specific market conditions are needed for the writing of a call option to make sense. The best option is to increase the share price. Then there is an increase in the value of the share portfolio and a decrease in the value of the acquired put option. An investor may feel that the rises are not sustained and should use market fluctuations to earn extra cash. Moreover, he does not intend to get rid of the stock portfolio because he believes that the company has a lot of potential ahead of it.
An example is the situation on August 3, 2022. The investor bought 100 Apple shares at an average price of $ 166. He is afraid that a correction is likely in the near future, but he does not want to sell the shares because he bought them "for the long term". To protect against declines, an investor purchased a December put option with an exercise price of $ 160 for $ 885 ($ 8,85 per share). By August 17, 2022, the rate had risen to $ 174,5. The investor decided to somehow lower the price of his collateral, leaving himself room for an increase in Apple's price. To this end, he issued a December call option with an exercise price of $ 190. He received $ 5,5 per share for it. This gives the investor room to increase the rate to around $ 195,5.
Writing a call option raised the drop protection point from $ 151,15 to $ 156,65. By September 30, Apple's stock had dropped to $ 138, a loss of $ 28 per share. The value of the issued call option dropped to $ 0,25 (profit of $ 5,25). In turn, the price of the put option rose to $ 23 (profit of $ 14,15). Thus, the collar yield was $ 19,4, which covered 69,3% of the loss generated by the options portfolio.
- insurance against drops in the covered call strategy
Covered call is a strategy that allows the investor to earn an "additional dividend" on the shares, which is the value of the issued call option. The strategy gives the investor additional profit from the stock portfolio in a situation when the instrument on which the options are issued moves in a sideways, downtrend or slightly rising trend. Of course, there is a way to manage your covered call strategy using the put option.
During an increase in the share price, the investor expects a downward correction. At the same time, it does not want to get rid of shares (long-term bias) and call options (a drop in the price is a profit for the writer of the call option). In order to profit from his predictions, the investor decides to buy a put option, which is to constitute an additional source of income in the event of a downturn scenario. The increase in the rate has made put options cheaper, which means that the investor can defend his portfolio against a drastic decline in value at a much more affordable price.
An example is the situation on August 3, 2022. The investor bought 100 Apple shares at an average price of $ 166. The buyer of the shares decided to create a covered call strategy by issuing a December call option with an exercise price of $ 190. He received a bonus of $ 3,2 per share for it. On August 17, the rate increased to $ 174,5. In order to protect the portfolio from declines, the investor decided to purchase a December put option with an exercise price of $ 175. He paid $ 11 for it, which meant the put option protected from falling below $ 164.
Adding the potential profit from the issued call option, the transaction has a guaranteed profit of $ 1,2 ($ 164 + $ 3,2-$ 166). The maximum profit per transaction is $ 16,2 ($ 190 + $ 3,2-$ 166-$ 11). By September 30, Apple's stock had dropped to $ 138, a loss of $ 28 per share. The value of the written call option dropped to $ 0,25 (profit of $ 2,95). In turn, the price of the put option rose to $ 37 (profit of $ 26). So the collar yield of $ 28,95 more than covered the loss on the stock portfolio.
How is the collar strategy different from bull spread?
Both strategies have a similar chart profile but are designed for different situations. Collar is a strategy for hedging a portfolio of shares, while bull spread is a directional strategy assuming an increase in the price of the underlying instrument.
Another difference is that creating a collar from options most often requires the involvement of additional capital (except when a non-cost collar is created) and in the case of a bull put spread, the investor receives funds in advance, which are the maximum profit (issuing a put with a higher strike price and buying put with a lower strike price).
Another difference is that the collar requires much more capital to be invested, because the investor must have stocks in advance that he wants to hedge against the risk of a decline in the price.
What is a non-cost collar?
This is a typical collar strategy but does not cost the investor or a dollar. The value of the call option you issued is simply greater than the put option you bought. As a result, the bonus received is greater than the cost of buying the put option. The result is that the security is theoretically "free". Of course, the hidden cost is limiting the potential for future profits.
The non-cost collar strategy is generally used with long-term options (ie LEAPS). It works best when the dividend yield is low and volatility is high. High volatility makes options "expensive". For this reason, writing a call option whose premium is higher than the put may be a good idea, because as the implied volatility of both options decreases, they will decline. As a result, the writer of the call option can report a nice profit even if the price of the underlying has not changed.
How to manage a collar?
The collar strategy seems simple, but it is worth managing it properly. What to do when option trades generate positive cash flow and stocks depreciate? Much depends on the trader's investment strategy and risk appetite. In order to explain this issue, it is worth using an example.
On April 7, 2022, an investor purchased 500 shares of Philips at an average price of € 28 per share. This means that the portfolio value was € 14. The investor expects Philips stock to perform weakly by the end of the year, but believes in the company in the long term. In order to hedge against declines, he purchased 000 December put options with an exercise price of € 5, paying a premium of € 27 (per share). Thus, the security costs € 2,78, which is as much as 1% of the portfolio value. To lower the costs of the strategy, the trader decided to issue 1390 December 10 call options with an exercise price of € 5. He received a € 30 (per share) bonus for them. As a result, the costs were reduced to 1,7 € or 540% of the value of the equity portfolio.
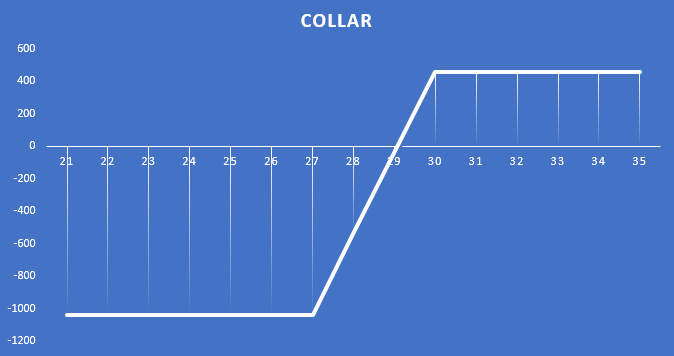
Source: own study
The presented strategy generates a maximum profit of € 0,92 per share, or € 460. This means that the strategy can generate a profit of 3,29%. Meanwhile, the maximum trade loss is € 2,08 per share, or € 1040. This meant that the investor could lose a maximum of 7,43%.
On August 8, 2022, Philips shares fell to € 20,31. The loss on the equity portfolio was € 7,69 per share, or € 3845. As a result, the value of this item in the portfolio decreased by 27,46%. Fortunately, the collar strategy worked, as shown in the table below:
| Price from 7.04.2022/XNUMX/XNUMX | Price from 8.08.2022/XNUMX/XNUMX | Profit on the transaction | |
| Put option | 2,78 | 6,95 | +4,17 |
| Call option | 1,70 | 0,06 | +1,64 |
Source: own study
The gain on the option bought and written was € 5,81 per share, or € 2905. Thus, the options covered most of the losses generated by the equity portfolio. Finally, the total collar strategy ended in a loss of € 1,88 per share, or € 940, representing a 6,71% decline in the value of the investment portfolio.
What can an investor do with such a position?
One of the easiest strategies is to keep your position unchanged. The advantage of this solution is that inactivity does not generate any additional transaction costs. The downside is a certain lack of optimization of the strategy in terms of the risk-reward ratio. Since the premium of the call option is worth € 6 (€ 0,06 * multiplier) there is no point in keeping that option for settlement. The potential additional profit is too small to put ourselves at risk of a sharp rise in the Philips price.
If an investor expects further declines to be unlikely, he may close out his calls and puts. As a result, he will own 500 Philips shares and € 2905 cash. The funds can be used to purchase further Philips shares. At a price of € 20,31, this would give a further 143 shares (excluding transaction costs). The disadvantage of this solution is the risk of further drops in the company's shares.
In the scenario of further declines, the investor may think about issuing further call options with a lower strike price. For example, on August 8, 2022, an investor could issue 5 December call options with an exercise price of € 22, receiving € 1 a share. With this strategy, in the event of further declines, the overall loss of the portfolio will be reduced to € 570. The cost, however, is the exposure to an increase in the Philips exchange rate. If it rises to € 27, the portfolio loss will be € 3070 (ie € 6,14 per share). This is because the trader will then lose a short position on call options, which are traded at € 22, and will lose profit on the currently profitable put position. Conversely, the additional sale of put options at € 6,95 per share will reduce the maximum profit to € 405 (€ 0,81 per share) and the portfolio will be exposed to a further decline in prices.
In order to better present the results of individual strategies, we will use the table. The following strategies are presented:
- A: leaving the strategy unchanged
- B: close of call and put options and purchase of 143 Philips shares at € 20,31
- C: closing the call and issuing a new call for the December series with an execution price of 22 €
- D: closing a call and put and issuing a new call option for the December series with an exercise price of € 22
- E: close options and keep cash
| Course = 15 € | Course = 20 € | Course = 25 € | Course = 30 € | |
| Stock portfolio | 6500€ | 4000€ | 1500€ | +1000€ |
| Strategy A | 1040€ | 1040€ | 1040€ | +460€ |
| Strategy B | 4355€ | 1140€ | +2075€ | +5290€ |
| Strategy C | 570€ | 570€ | 2070€ | 3070€ |
| Strategy D | 3095€ | 595€ | +405€ | +405€ |
| Strategy E | 3595€ | 1095€ | +1405€ | +3905€ |
Source: own study
As you can see, strategies C and D seem to be the least profitable, because rolling call options kills the potential to generate profit in the event of a trend change in the Philips price. Strategy D is terrible as it no longer protects against a further decline in the share price and achieves less profit than in the case of strategy A (doing nothing). The only advantage of Strategy D is that you earn an extra € 500 if the rate stays around € 20 between August and December.
Summation
It is certainly not a strategy that will deliver stunning rates of return, but that is not its purpose. The collar strategy can be an interesting idea to protect your portfolio against the risk of a sharp sell-off. Under appropriate conditions, such a strategy can be created at no cost because the premium value of the issued call option will be greater than the value of the purchased put option.
Do you know that…?
Saxo Bank is one of the few Forex brokers that offers vanilla options. The investor has a total of over 1200 options at his disposal (currencies, stocks, indices, interest rates, raw materials). CHECK






















![Forex Club – Tax 9 – Settle tax on a foreign broker [Download the Application] Forex Club - Tax 9](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2024/02/Forex-Club-Podatek-9-184x120.jpg?v=1709046278)
![Trading View platform – solutions tailored to the needs of traders [Review] trading view review](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2024/03/trading-view-recenzja-184x120.jpg?v=1709558918)
![How to connect your FP Markets account to the Trading View platform [Guide] fp markets trading view](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2024/02/fp-markets-trading-view-184x120.jpg?v=1708677291)
![How to invest in ChatGPT and AI? Stocks and ETFs [Guide] how to invest in chatgpt and artificial intelligence](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2023/02/jak-inwestowac-w-chatgpt-i-sztuczna-inteligencje-184x120.jpg?v=1676364263)


![WeWork – the anatomy of the collapse of a company valued at $47 billion [WeWork, part II] wework bankruptcy story](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/wework-bankructwo-historia-184x120.jpg?v=1711729561)
![Adam Neumann – the man who screwed up Softbank [WeWork, part AND] adam neumann wework](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/adam-neumann-wework-184x120.jpg?v=1711728724)





![How to transfer shares to another brokerage office [Procedure description] how to transfer shares to another brokerage house](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2024/03/jak-przeniesc-akcje-do-innego-biura-maklerskiego-184x120.jpg?v=1709556924)

![The most common mistakes of a beginner trader - Mr Yogi [VIDEO] Scalping - The most common mistakes of a beginner trader - VIDEO](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2024/03/Scalping-Najczestsze-bledy-poczatkujacego-tradera-VIDEO-184x120.jpg?v=1711601376)
![Learning patience: No position is also a position - Mr Yogi [VIDEO] Scalping - Learning patience - No position is also a position - VIDEO](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2024/03/Scalping-Nauka-cierpliwosci-Brak-pozycji-to-tez-pozycja-VIDEO-184x120.jpg?v=1710999249)
![When to exit a position and how to minimize losses - Mr Yogi [VIDEO] Scalping - When to exit a position and how to minimize losses - VIDEO](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2024/03/Scalping-Kiedy-wyjsc-z-pozycji-i-jak-minimalizowac-straty-VIDEO-184x120.jpg?v=1710336731)






![How to invest in Feeder Cattle? [Guide] how to invest in livestock - feeder cattle](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2023/09/jak-inwestowac-w-bydlo-hodowlane-feeder-cattle-300x200.jpg?v=1693821591)


